Future of Clinical Research in the Digital Age
Clinical research is undergoing a transformative shift in 2025, driven by rapid advancements in digital technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI), remote trials, virtual monitoring, and modern tools are redefining how studies are conducted, making them more efficient, patient-centric, and data-driven. This blog delves into the current trends, innovations, and future directions shaping the digital landscape of clinical research.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Trials
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept in healthcare—it’s a current-day force reshaping how clinical trials are planned, conducted, and evaluated. In 2025, the use of AI in clinical research has grown beyond algorithmic predictions to a comprehensive ecosystem of predictive modeling, automated data handling, and intelligent patient engagement.
Enhancing Study Design and Recruitment
One of the most critical stages in any clinical trial is the design and recruitment phase. Traditionally, researchers relied on manual data review, past research, and educated estimations to define study parameters. This process was time-consuming and prone to human error or oversight.
With AI, this paradigm has changed dramatically. Here’s how:
AI-powered algorithms can scan through millions of data points from historical trials, electronic health records (EHRs), genomic databases, and real-world evidence (RWE) to suggest:
Optimal primary and secondary endpoints (e.g., measurable outcomes that indicate a drug's effectiveness).
Ideal sample sizes for statistical relevance without overburdening the trial logistics.
Precise eligibility criteria, including demographic, clinical, and even genetic markers to select the most suitable patient populations.
Machine learning (ML) models, a subset of AI, are particularly useful for identifying complex patterns and correlations that humans might miss—like how a patient’s genetic makeup could impact drug metabolism or how comorbidities may affect trial outcomes.
Tools like predictive analytics platforms can simulate different trial scenarios and forecast potential outcomes, enabling researchers to design more efficient and targeted trials with fewer risks of failure.
📌 In 2025, companies are also integrating natural language processing (NLP) to scan unstructured medical notes and extract relevant data for trial inclusion.
Streamlining Data Analysis
Clinical trials generate massive volumes of data, often across multiple formats and platforms. The conventional method of manual data entry, followed by spreadsheet analysis, is not only labor-intensive but also slow and prone to error.
Here’s how AI streamlines data analysis:
Real-Time Monitoring: AI systems continuously monitor data as it's collected—whether it’s from ePROs (electronic patient-reported outcomes), wearable devices, or lab systems. If there's a deviation from expected values (e.g., sudden spike in blood pressure or abnormal lab values), the system flags it immediately, enabling quick action.
Anomaly Detection: Advanced AI models are trained to recognize outliers and potential data integrity threats—like duplicate entries, inconsistent values, or uncharacteristic patient behavior—ensuring the validity of results.
Data Harmonization: AI algorithms automatically clean, structure, and standardize raw data, making it easier to integrate results from various trial sites, geographies, or formats.
Bias Reduction: ML tools can highlight areas where data may reflect systemic bias (e.g., overrepresentation of one demographic group), allowing researchers to take corrective steps.
Accelerated Insights: By shortening the data analysis timeline from months to weeks—or even days—AI enables quicker interim analyses, early safety assessments, and potential early termination of unsuccessful studies, which saves both time and cost.
📌 In 2025, regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA are showing growing openness toward AI-validated data structures—provided transparency and auditability are in place.
Additional 2025 Innovations to Know:
AI dashboards can generate automated progress reports for sponsors and CROs (Contract Research Organizations), offering real-time visibility into participant status, dropout rates, and protocol adherence.
Some platforms are using federated learning, a cutting-edge ML approach that allows models to be trained across multiple decentralized data sources without moving data itself—thus preserving patient privacy while still learning from diverse datasets.
Digital twins—virtual replicas of patient biology—are being created using AI to simulate treatment effects before actual human testing begins, improving protocol customization.
Embracing Remote and Decentralized Trials
In 2025, remote and decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) are no longer a trend—they're becoming the standard model for modern research. Enabled by digital tools, telemedicine, and remote monitoring technology, DCTs shift the clinical trial environment from hospitals and clinics to the comfort of a patient’s home.
This evolution is designed to improve trial accessibility, diversity, efficiency, and compliance, addressing long-standing barriers in traditional site-based studies.
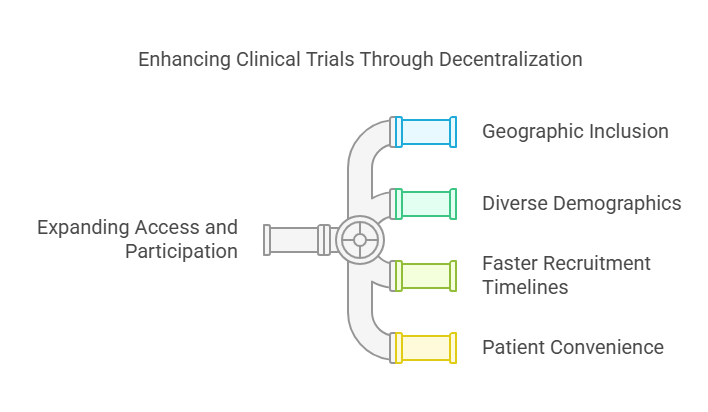
Expanding Access and Participation
One of the greatest challenges in traditional clinical trials is recruitment and retention. Historically, trials have been limited to major medical centers, leaving out patients in rural, underserved, or international locations.
Decentralized trials solve this in several key ways:
1. Geographic Inclusion
Patients no longer need to live near a research facility. Remote trials remove the burden of traveling long distances, which is particularly impactful for:
Elderly or mobility-impaired participants
Patients in rural or remote areas
Working individuals who can't afford to take time off
2. Diverse Demographics
By reducing the need for in-person visits, DCTs improve the diversity of participants—both ethnically and socioeconomically. This helps ensure that new treatments are tested across a broader spectrum of the population, making findings more generalizable and inclusive.
3. Faster Recruitment Timelines
AI-powered recruitment platforms (like those used in DCTs) match patients with trials based on EHRs, digital advertising, and self-reported health data. This speeds up recruitment and improves screening accuracy.
4. Patient Convenience = Better Retention
Trials that don’t disrupt a participant's daily life tend to have higher retention and compliance rates. Participants are more likely to stick with the study if it fits their schedule and lifestyle.
Leveraging Telemedicine and Wearables
Decentralization goes hand-in-hand with telemedicine and wearable technology, which are crucial in maintaining patient monitoring and safety outside the clinic.
1. Telemedicine Consultations
Participants engage with researchers and healthcare professionals through secure video platforms or mobile apps. This ensures:
Ongoing clinical assessments without physical visits
Real-time discussions about side effects or concerns
Virtual informed consent processes
This has become even more critical in 2025 as digital literacy continues to rise, and remote care becomes normalized post-pandemic.
2. Wearable Devices for Continuous Monitoring
Smartwatches, biosensors, patches, and even AI-integrated fitness trackers now play an essential role in trials. These wearables collect:
Heart rate, ECG, blood pressure
Oxygen saturation
Sleep patterns
Physical activity levels
Glucose levels (in diabetic trials)
These devices feed real-time data to centralized trial dashboards, allowing clinicians to:
Monitor treatment effects closely
Respond to adverse events immediately
Ensure patient compliance with the protocol
3. Remote Sample Collection
Companies are also integrating at-home lab sample collection kits for blood, saliva, or swabs. These can be mailed to labs or picked up by healthcare workers, ensuring continuity in data collection without in-person visits.
📌 Example in Action:
A patient enrolled in a virtual oncology trial might use a smartwatch to log vital signs, an app to report side effects, and attend weekly check-ins with the research nurse via Zoom—all without stepping foot in a clinic.
Added Benefits of Remote Trials in 2025
Environmental Impact: Fewer clinic visits mean a smaller carbon footprint.
Cost Savings: Lower operational costs for sponsors and reduced patient-related travel expenses.
Global Expansion: With regulatory alignment progressing (especially with agencies like the FDA and EMA), multi-country virtual trials are more feasible than ever.
Virtual Monitoring and Digital Tools
In the evolving world of clinical research, virtual monitoring and digital health tools are transforming how data is collected, managed, and acted upon. These technologies are not only enhancing clinical trial efficiency but also reshaping the patient experience—making trials more interactive, responsive, and patient-centric.
Let’s break this down:
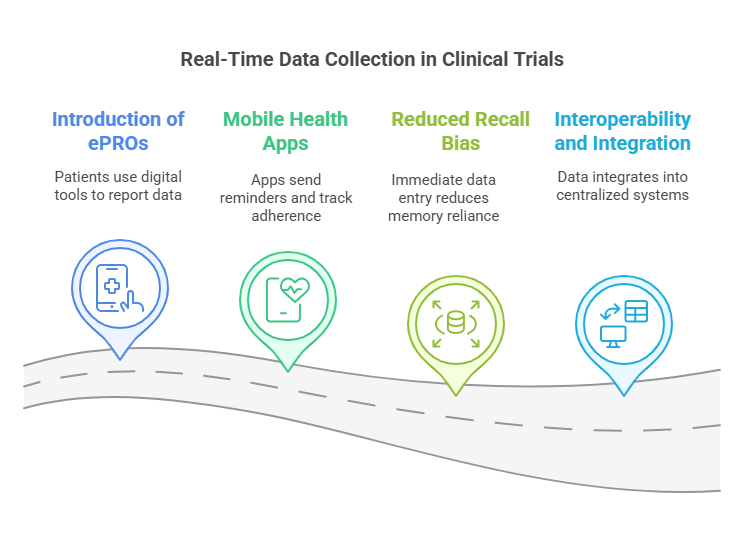
Real-Time Data Collection
Traditionally, trial data was collected during scheduled site visits, which led to infrequent reporting, data delays, and recall bias (patients forgetting or misreporting events between visits). In 2025, digital health tools have made real-time data collection a reality.
1. Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes (ePROs)
ePROs allow participants to self-report symptoms, side effects, and quality-of-life measures using smartphones, tablets, or web platforms.
These inputs are captured instantly, reducing dependency on in-person visits and improving data timeliness.
The FDA and EMA now accept ePRO data as a valid source of patient-centric evidence when collected via validated systems.
🧠 Example: A patient in a migraine study can report headache severity on an app as soon as symptoms start, ensuring real-time accuracy rather than relying on memory during a monthly clinic visit.
2. Mobile Health Apps
Apps designed for specific clinical trials often come with push notifications, medication reminders, and questionnaire prompts, helping participants stay compliant.
They allow researchers to track adherence metrics, such as when doses were taken or missed, in real-time.
3. Reduced Recall Bias
Because data is entered on-the-spot, patients don’t have to remember when symptoms occurred or how intense they were.
This improves data reliability and reduces the statistical noise that can affect outcome measures.
4. Interoperability and Integration
Real-time data from ePROs and mobile apps can be integrated into centralized trial management systems (e.g., CTMS, EDC), allowing sponsors and monitors to access updates immediately.
Enhancing Patient Engagement
High patient engagement is a critical success factor for modern clinical trials. Engaged participants are more likely to stay compliant, complete the study, and provide more accurate data. Digital platforms are enhancing this engagement in innovative ways.
1. Interactive Platforms
Portals with chat features, telemedicine integration, study dashboards, and progress trackers give participants more control and visibility into their trial journey.
Participants can ask questions, receive answers from study staff, and access educational materials anytime.
🧠 Example: In a long-term diabetes trial, participants might use a platform that shows their glucose trends, tracks their medication intake, and provides weekly updates on trial milestones—all from a single dashboard.
2. Gamification and Incentives
Some apps use gamified features—such as daily streaks, badges, or reward points—to keep participants motivated.
In 2025, ethical incentive programs built into digital platforms are improving retention across multi-year studies.
3. Better Communication = Better Retention
Frequent, two-way communication through messaging apps or video consults fosters a sense of involvement and support, reducing dropout rates.
Engaged participants also feel valued and heard, leading to more meaningful contributions and improved overall satisfaction.
4. Remote Check-Ins & Feedback Loops
Participants can give feedback on the trial experience itself, which helps study coordinators refine the protocol and address issues proactively.
Many sponsors now offer personalized progress reports, so participants can see how their involvement is making a difference.
Explore Courses for Clinical Research Career
Courses Available:
Conclusion
As we move deeper into the digital age, clinical research is undergoing a profound transformation. From AI-driven trial design to remote participation, virtual monitoring, and real-time data collection, modern tools are making studies more efficient, inclusive, and patient-centric. These innovations not only improve data quality but also enhance the overall experience for participants and researchers alike. Embracing this digital evolution is essential for advancing global health outcomes—and organizations like CCRPS are at the forefront of this change, equipping professionals with the training and tools needed to lead in this new era of clinical research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Decentralized trials offer increased accessibility, improved patient engagement, and faster recruitment by allowing participants to engage remotely.
-
AI enhances efficiency by optimizing study designs, predicting outcomes, and facilitating real-time data analysis.
-
Challenges include ensuring data security, maintaining regulatory compliance, and addressing technological disparities among participants.
-
Data protection measures include encryption, secure data storage, and adherence to privacy regulations like GDPR.