What is an Institutional Review Board (IRB) and Why Does It Matter?
In clinical research, ethical considerations are as important as scientific rigor. One of the most crucial components of ensuring ethical standards in clinical trials is the Institutional Review Board (IRB). But what exactly is an IRB, and why does it play such a pivotal role in research? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of the IRB, its functions, and its impact on clinical research. Whether you're a researcher, participant, or someone interested in the clinical trials process, understanding the role of an IRB is essential.
Introduction: The Ethical Backbone of Clinical Research
Picture this: a researcher has a groundbreaking new drug that could potentially cure a life-threatening disease. Before testing it on humans, how do we ensure that the drug is both effective and safe? Enter the Institutional Review Board, or IRB. Think of the IRB as the "ethical watchdog" of clinical trials, ensuring that research follows strict ethical guidelines to protect the rights and safety of participants.
While science advances at an unprecedented pace, the importance of ethical oversight cannot be overstated. Clinical trials can only move forward when an IRB reviews and approves the study, ensuring that the research is conducted ethically, transparently, and in compliance with regulatory standards.
Bonus Read: Learn more about the role of medical review in pharmacovigilance and its critical importance in ensuring the safety of clinical trial participants.
What is an Institutional Review Board (IRB)?
An Institutional Review Board (IRB) is a group of experts and professionals—such as doctors, scientists, ethicists, and legal advisors—that is responsible for reviewing and overseeing research studies involving human participants. The primary purpose of an IRB is to ensure that the study respects participants' rights, ensures their safety, and upholds ethical standards in line with national and international regulations.
IRBs operate under the guidelines set by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and other regulatory bodies. These boards review study protocols, consent forms, and participant recruitment procedures to guarantee that research is both scientifically sound and ethically conducted.
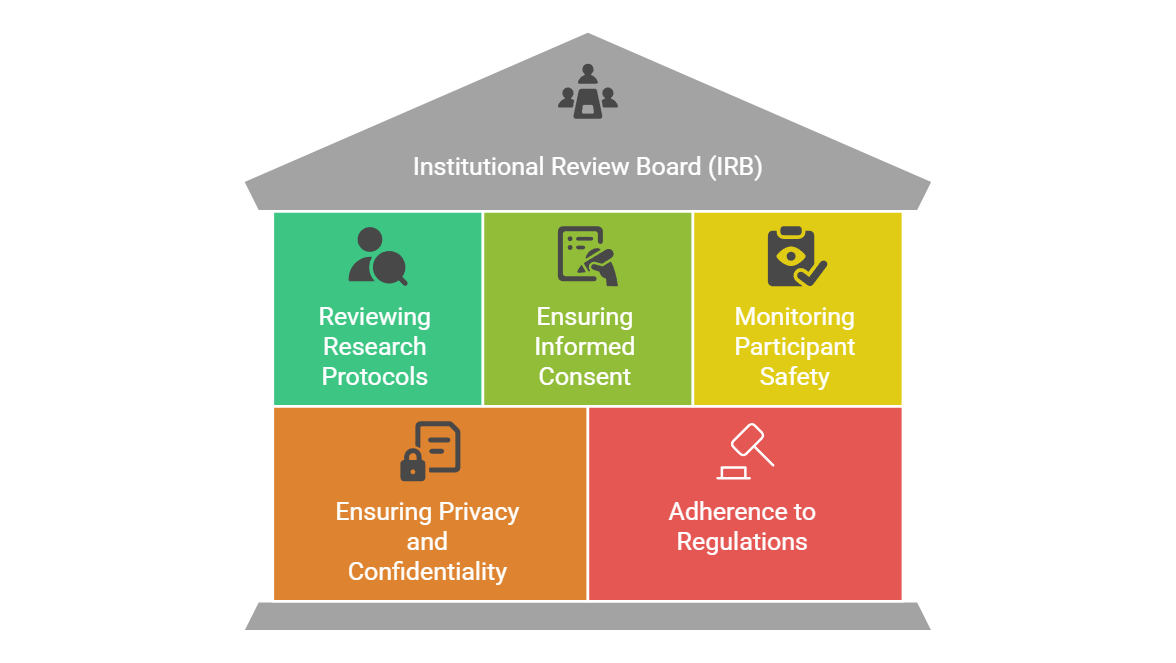
Key Roles and Responsibilities of an IRB
The IRB has several critical functions in the clinical research process. Let's explore these in detail:
1. Reviewing Research Protocols
Before any clinical trial involving human participants begins, the IRB must review the study's research protocol. This includes evaluating the objectives, methods, and potential risks associated with the research. The IRB ensures that the research design is scientifically valid and that the risk to participants is minimized.
2. Ensuring Informed Consent
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical research. The IRB evaluates the consent documents to ensure that participants fully understand the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits of the study. Informed consent ensures that participants voluntarily agree to take part in research, knowing the risks involved.
3. Monitoring Participant Safety
The IRB has an ongoing role in monitoring participant safety throughout the duration of a clinical trial. This includes reviewing adverse event reports and evaluating the risk-benefit ratio of continuing the trial. If new risks emerge or participants are harmed, the IRB can request modifications or even halt the trial.
4. Ensuring Privacy and Confidentiality
The IRB ensures that the confidentiality of participants is upheld throughout the trial. This involves ensuring that sensitive health data is protected and that personal information is handled according to ethical and legal standards.
5. Adherence to Regulations and Guidelines
The IRB ensures that the study complies with federal, state, and institutional regulations. They also ensure that ethical principles outlined in documents like the Declaration of Helsinki and the Belmont Report are adhered to. These regulations guide researchers to act with respect, beneficence, and justice in their interactions with participants.
Why Does an IRB Matter in Clinical Research?
Now that we understand what an IRB is and its primary functions, it’s essential to recognize why it is so vital to clinical research.
1. Protecting Human Subjects
The most important function of an IRB is to protect human subjects. Clinical trials, while necessary for scientific progress, involve risks. The IRB ensures that these risks are minimized, and that participants are fully informed about what they are consenting to. Without an IRB, researchers may unknowingly or deliberately put participants at risk for the sake of the study.
2. Ensuring Ethical Research Practices
Clinical trials can sometimes be fraught with ethical dilemmas, such as balancing the potential benefits of a treatment with the risks to participants. The IRB ensures that studies are conducted in a manner that respects the dignity and autonomy of participants, as well as the ethical guidelines of the research community.
3. Building Public Trust
Public trust in medical research is essential for the success of clinical trials. When participants know that an independent body, such as the IRB, is reviewing the study and ensuring their safety, they are more likely to participate in future trials. This builds confidence in the scientific process and encourages wider participation in clinical research.
4. Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Adherence to regulations is a key component of clinical research. The IRB ensures that the study complies with federal and institutional guidelines, which not only protects participants but also keeps the research process legally sound. This helps prevent legal consequences and ensures the results of the trial are valid and credible.
5. Preventing Exploitation of Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups, such as children, the elderly, or individuals with cognitive impairments, are considered vulnerable populations in clinical research. The IRB ensures that extra safeguards are in place to protect these individuals and prevent their exploitation.
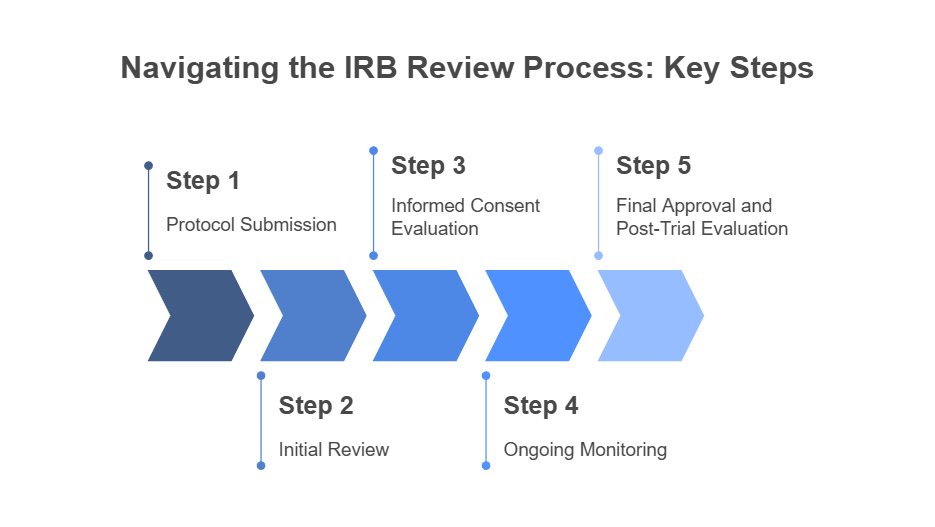
The IRB Review Process: Step-by-Step
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) review process is designed to ensure that clinical research studies are ethically sound and protect the rights and welfare of participants. The process involves several key steps:
Step 1: Protocol Submission
Researchers submit their study protocol to the IRB for review. This includes details on the study's design, participant criteria, risks, and procedures.
Step 2: Initial Review
The IRB reviews the protocol to ensure it adheres to ethical guidelines and federal regulations. This review may involve discussions and feedback from committee members.
Step 3: Informed Consent Evaluation
The IRB evaluates the informed consent form to ensure participants are fully informed about the study, risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw.
Step 4: Ongoing Monitoring
Once the study is approved, the IRB continues to monitor the research. They receive regular updates on adverse events, protocol deviations, and any changes to the study.
Step 5: Final Approval and Post-Trial Evaluation
At the end of the study, the IRB evaluates the results and assesses the overall safety of the trial. They may request follow-up reports or additional studies to further analyze the findings.
Pro Tip: To understand how social media data is utilized for pharmacovigilance, you can explore the latest advancements in leveraging online platforms for adverse event reporting.
Common Myths About IRBs
There are several misconceptions about Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) that may lead to confusion for researchers and the general public. Let’s debunk a few of them:
Myth 1: IRBs only approve drug trials
While IRBs are commonly associated with drug trials, they also review a wide range of studies, including behavioral research, medical device trials, and even some social science studies.
Myth 2: IRB approval is a one-time event
IRB approval is not a one-time event. It requires ongoing monitoring throughout the trial to ensure continued participant safety and regulatory compliance.
Myth 3: Researchers can bypass the IRB if they have the necessary experience
No matter how experienced a researcher is, IRB approval is mandatory for all research involving human subjects. This ensures that ethical standards are maintained.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of the IRB in Clinical Research
In conclusion, the Institutional Review Board (IRB) plays a vital role in safeguarding the integrity of clinical research and protecting the rights of participants. Whether it's evaluating research protocols, ensuring informed consent, or monitoring ongoing studies, the IRB ensures that ethical standards are upheld throughout the clinical trial process. By maintaining these standards, the IRB helps build public trust in research and allows clinical trials to progress in a safe and ethical manner.
When embarking on a career in clinical research, understanding the IRB process is crucial for maintaining the highest standards of ethics and compliance. It’s not just about gathering data; it’s about ensuring that the research is conducted with the utmost respect for human participants.
Stay updated with the latest clinical research trends and certification programs at CCRPS, where we offer comprehensive clinical research training and certification courses designed to elevate your career and ensure compliance in the industry.
-
An Institutional Review Board (IRB) is a group of experts that ensures research involving human participants is conducted ethically and in compliance with regulations.
-
IRB approval is required to protect participants’ rights, ensure their safety, and ensure that the study follows ethical and regulatory standards.
-
The time for IRB approval varies, but it generally takes a few weeks to several months depending on the complexity of the research.
-
An IRB typically includes doctors, scientists, ethicists, legal professionals, and community members, ensuring a well-rounded evaluation process.
-
Conducting a clinical trial without IRB approval is a violation of regulations and can result in the termination of the trial and legal consequences for the researchers.
-
IRB decisions are not always final. If a study is rejected or modified, researchers can revise their protocols and resubmit for approval.
-
Any research involving human participants, including drug trials, medical device studies, and behavioral research, requires IRB approval.
-
Yes, an IRB can reject a study if it determines that the research does not meet ethical standards, fails to minimize risks to participants, or does not comply with regulatory guidelines.