Clinical Research Quality Assurance
Clinical research is pivotal in healthcare innovation, leading to new treatments and therapies that drastically improve patient outcomes. Quality assurance in clinical trials plays a crucial role by ensuring these innovations are carried out ethically and scientifically. Professionals in clinical quality assurance ensure all study aspects comply with stringent regulatory standards, safeguarding patient safety and upholding data integrity.
Regulatory Requirements in Clinical Quality Assurance
The system overseeing quality assurance, in studies is complex. Includes various regulations at internal and global levels as well as within countries.The guidelines set by the International Conference on Harmonisation. Good Clinical Practice (ICH GCP)serves as a standard for maintaining quality in research and is important for obtaining regulatory approvals, across the globe.
Government organizations such, as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) along with the European Medicines Agency (EMA) establish guidelines to guarantee the execution of clinical trials and greatly influence the assurance quality in clinical trials field. Non compliance can result in consequences such as pausing trials financial fines, and harm, to reputation.
Professional Roles and the Importance of Clinical Quality Assurance Certification
In the field of clinical quality assurance professionals are tasked with ensuring that all regulatory standards are adhered to Monitoring study protocols and carrying out audits play a role, in upholding the integrity of the trial It is widely advised that individuals engaged in clinical trials obtain certification, in clinical quality assurance to demonstrate proficiency in GCP and regulatory adherence.
Educational Pathways and Specialized Clinical Quality Assurance Training Courses
In the realm of research quality control methods usually kick off with a base, in life sciences coupled with specialized education in regulatory matters Training programs for clinical quality assurance like the ICH GCP course play a pivotal role, in boosting professional qualifications and adherences to global benchmarks.
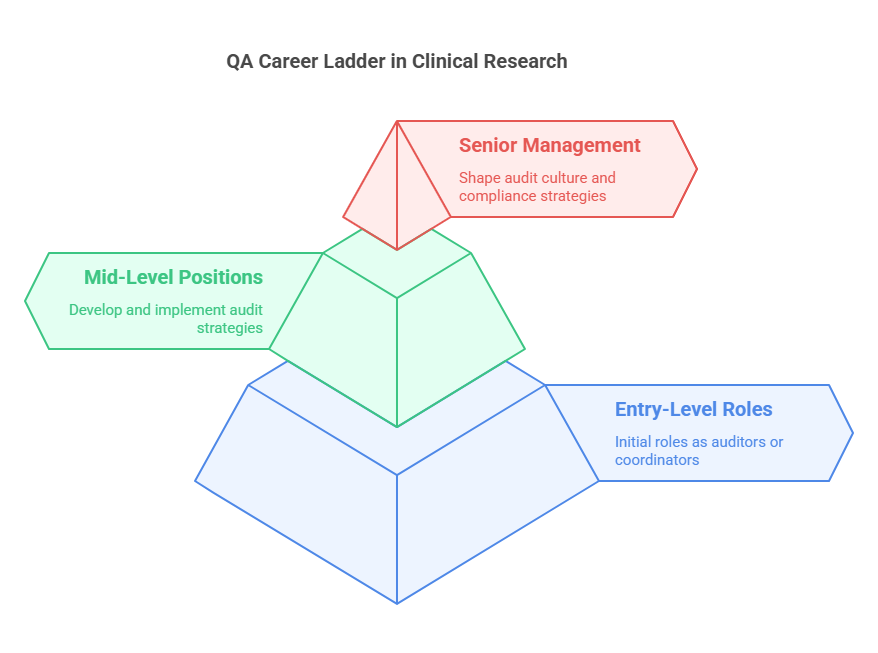
Career Progression in Quality Assurance
The path of a quality assurance professional in Clinical Research Coordinator can vary widely but generally follows a progression from entry-level to senior management roles. Initially, QA professionals may start as auditors or coordinators, focusing on specific trials or aspects of compliance. As they gain experience, they often move into more strategic roles.
Mid-level QA positions might involve:
Developing and implementing audit strategies and plans.
Overseeing audit teams.
Ensuring continuous compliance with all applicable regulations.
At the senior level, QA professionals might take on roles such as QA Director or Head of Compliance. These positions involve:
Shaping the audit culture within an organization.
Making high-level decisions regarding compliance strategies.
Leading interactions with regulatory authorities.
Each step on the career ladder requires a deeper understanding of both the scientific and regulatory nuances of clinical trials, as well as enhanced leadership and strategic planning skills.
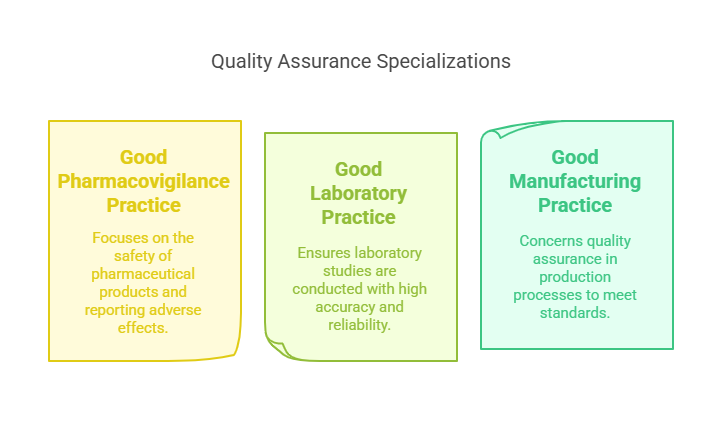
Specializations and CRO Quality Assurance
Diversifying skills in areas like Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GPvP) and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) expands a QA professional's capabilities, making them more versatile and attractive to employers. Specialization in CRO quality assurance ensures that contract research organizations maintain high standards in conducting trials, crucial for client trust and regulatory compliance.
Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GPvP): Focuses on the safety of pharmaceutical products, ensuring that all adverse effects are correctly reported and analyzed.
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP): Ensures that laboratory studies, such as toxicity tests, are conducted with high standards of accuracy and reliability.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP): Concerns the quality assurance of production processes, guaranteeing that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
Gaining experience in more than one of these areas can significantly enhance a QA professional's career, offering broader opportunities and making them more attractive to employers. Specializing in a highly sought-after area like GPvP, given its critical role in patient safety, can be particularly beneficial.
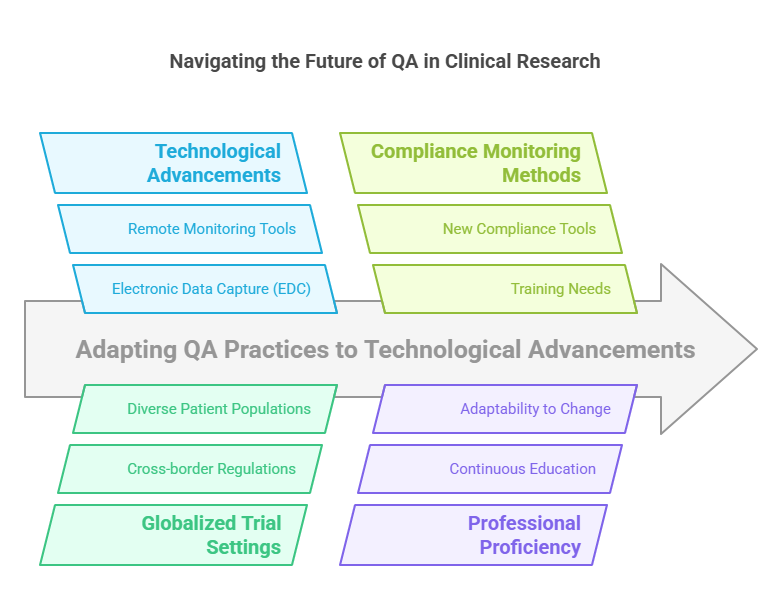
The Future of QA in Clinical Research
The future of quality assurance in clinical research involves adapting to technological advancements and globalized trial settings. Digital tools like electronic data capture (EDC) and remote monitoring technologies are transforming QA practices, requiring professionals to stay proficient with new compliance monitoring methods.
Addressing Challenges in Clinical Quality Assurance
The landscape of clinical quality assurance is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements and the increasing complexity of clinical trials. As the field grows, QA professionals must navigate a variety of challenges:
Technological Advancements: The integration of digital tools such as Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems and remote monitoring technologies has revolutionized clinical trial quality assurance. These tools require QA professionals to develop new skills and adapt to sophisticated methods of data oversight.
Globalization of Clinical Trials: With more clinical studies being conducted on an international scale, quality assurance in clinical trials must meet diverse regulatory requirements across different countries. This complexity necessitates a deep understanding of international guidelines and an ability to manage quality across varied regulatory landscapes.
Increasing Regulatory Scrutiny: As regulatory bodies intensify scrutiny to ensure patient safety and data integrity, the role of QA in clinical research becomes more demanding. Professionals must stay ahead of regulatory changes and ensure that all aspects of a trial are compliant.
Leveraging Opportunities in Clinical Quality Assurance
Despite these challenges, there are significant opportunities for growth and advancement within the field:
Certification and Continuous Learning: Obtaining a clinical quality assurance certification is more than a credential; it's an opportunity for professionals to deepen their knowledge and stay current with industry standards. Continuous learning through clinical quality assurance training courses is essential to keep pace with the field's evolution.
Specialization: Developing expertise in specific areas such as CRO quality assurance can open doors to specialized roles that are in high demand. This specialization allows professionals to focus on niche areas of QA, such as pharmacovigilance or manufacturing practices, increasing their value to employers.
Cross-functional Collaboration: QA professionals often work closely with other departments to ensure compliance and efficacy in clinical trials. This collaboration enhances their understanding of the broader clinical research process and builds a comprehensive skill set that benefits their career progression.
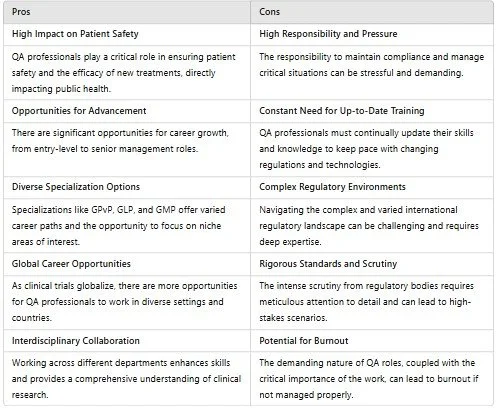
Pros and Cons of a Career in Clinical Quality Assurance
Conclusion
Clinical Quality Assurance (QA) is essential in healthcare, ensuring Clinical Trials Assistant Training course meet strict standards to safeguard patient safety and maintain the integrity of medical research. Despite its challenges, the field offers rewarding opportunities for career advancement and specialization, particularly in areas like pharmacovigilance and regulatory compliance. At CCRPS, we understand the critical role QA professionals play in driving healthcare innovations forward. For those ready to navigate the complexities of this vital industry, a career in Clinical Quality Assurance offers both significant professional growth and the unique satisfaction of making a real difference in patient care.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQS)
What is Clinical Research Quality Assurance?
Clinical Research Quality Assurance (QA) involves systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of a project to ensure that standards of quality are being met. It ensures that clinical trials are conducted in compliance with regulatory guidelines, Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and ethical standards to safeguard patient safety and data integrity.
Why is Quality Assurance important in clinical trials?
QA is crucial in clinical trials because it ensures the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of clinical data. It also guarantees that the rights, safety, and well-being of trial participants are protected. QA practices help prevent errors and inconsistencies, ensuring that the results of the trial are credible and can be used to support regulatory approvals.
What are the main responsibilities of a QA professional in clinical research?
QA professionals are responsible for developing quality standards and audit plans, conducting audits, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, training staff on GCP, and reviewing study-related documentation. They also handle corrective actions when compliance issues are identified.
What qualifications are needed to work in Clinical Research Quality Assurance?
Typically, a degree in life sciences, pharmacy, or medicine is required. Additional certifications in Quality Assurance, such as Certified Quality Auditor or Certified Quality Improvement Associate, and knowledge of GCP guidelines are highly recommended. Experience in clinical research or regulatory affairs is also beneficial.
How does one get certified in Clinical Research Quality Assurance?
Certification can be obtained through various professional bodies that offer courses and exams in Quality Assurance and Good Clinical Practice. Examples include the Society of Quality Assurance (SQA) and the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP). These certifications often require passing an exam and may require ongoing education to maintain.
What are the career prospects in Clinical Research Quality Assurance?
The demand for QA professionals in clinical research is strong due to the critical nature of compliance in clinical trials. Career prospects range from QA specialists and coordinators to managers and directors of QA in pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), and regulatory agencies. The role can also lead to opportunities in other areas of regulatory affairs and clinical operations.
How is technology changing the field of Clinical Research Quality Assurance?
Technology, especially digital tools like Electronic Data Capture (EDC), Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS), and remote monitoring solutions, is transforming QA by improving the efficiency and accuracy of data collection, audit trails, and overall compliance monitoring. These tools enable more robust data integrity checks and facilitate real-time compliance oversight.