Expert Tips for Overcoming Clinical Trial Data Management Challenges
Clinical trials are increasingly data-intensive, with the rise of digital health technologies, real-world evidence, and global patient recruitment. By 2025, managing clinical trial data has become more complex due to evolving regulatory landscapes, cybersecurity threats, and the sheer volume of data generated. This comprehensive guide explores expert strategies to address key challenges in clinical trial data management, including handling large data volumes, resolving data inconsistencies, navigating regulatory hurdles, and mitigating data breaches.
Managing Large Volumes of Data
The explosion of data from electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and genomic sequencing has transformed clinical trials. Managing this "big data" requires robust strategies to ensure data quality, integrity, and usability.
Challenges:
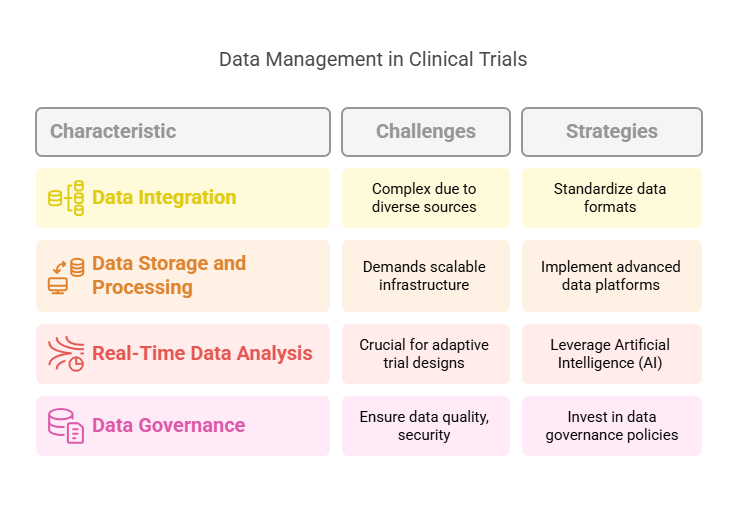
Data Integration: Combining data from diverse sources like EHRs, mobile apps, and laboratory systems can be complex.
Data Storage and Processing: Storing and processing large datasets demand scalable infrastructure.
Real-Time Data Analysis: Timely analysis is crucial for adaptive trial designs and decision-making.
Strategies:
Implement Advanced Data Platforms: Utilize cloud-based platforms and data lakes to store and manage large datasets efficiently.
Leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and predicting outcomes.
Standardize Data Formats: Adopt standardized data formats and ontologies to facilitate data integration and interoperability.
Invest in Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies to ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Related Blog: The Basics of Clinical Trial Data Management
Dealing with Data Inconsistencies
Data inconsistencies, such as missing or conflicting information, can compromise the validity of clinical trial results. Addressing these issues is essential for maintaining data integrity.
Challenges:
Missing Data: Participants may drop out or fail to report certain information, leading to gaps.
Conflicting Data: Discrepancies between data sources can arise due to errors or variations in data collection methods.
Strategies:
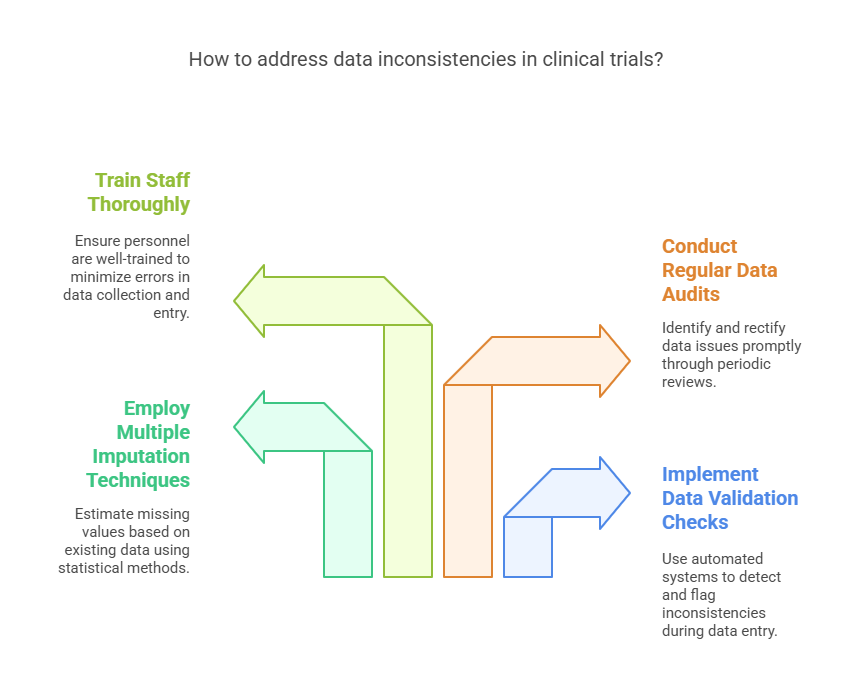
Implement Data Validation Checks: Use automated systems to detect and flag inconsistencies during data entry.
Employ Multiple Imputation Techniques: Statistical methods can estimate missing values based on existing data.
Conduct Regular Data Audits: Periodic reviews help identify and rectify data issues promptly.
Train Staff Thoroughly: Ensure that all personnel involved in data collection and entry are well-trained to minimize errors.
Navigating Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory requirements for clinical trials are continually evolving, with agencies like the FDA and EMA updating guidelines to enhance patient safety and data transparency. Staying compliant is critical to avoid delays and penalties.
Challenges:
Frequent Regulatory Updates: Keeping up with changes in regulations across different jurisdictions can be daunting.
Complex Approval Processes: Navigating the approval process requires meticulous documentation and adherence to protocols.
Strategies:
Maintain a Regulatory Intelligence System: Stay informed about regulatory changes through dedicated monitoring systems.
Engage Regulatory Experts: Consult with professionals who specialize in regulatory affairs to ensure compliance.
Standardize Documentation: Use standardized templates and checklists to ensure all regulatory requirements are met.
Implement Quality Management Systems (QMS): A robust QMS can help manage compliance-related activities effectively.
Handling Data Breaches
Data breaches pose significant risks to clinical trials, potentially compromising patient confidentiality and data integrity. Proactive measures are essential to prevent and respond to such incidents.
Challenges:
Cybersecurity Threats: Clinical trial data is a lucrative target for cybercriminals.
Insider Threats: Unauthorized access or misuse of data by internal personnel.
Strategies:
Implement Robust Security Protocols: Use encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect data.
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Periodic assessments help identify vulnerabilities and implement corrective actions.
Develop an Incident Response Plan: Prepare a comprehensive plan outlining steps to take in the event of a data breach.
Train Employees on Data Security: Educate staff about best practices and protocols to prevent breaches.
Related Blog: How to Implement Effective Clinical Trial Management Solutions?
Lesser-Known Facts About Clinical Trial Data Management
AI Integration: By 2025, AI is expected to manage 50% of trial data tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. (Source)
Data Breach Prevalence: Approximately 70% of clinical trials have experienced data breaches, highlighting the need for robust security measures. (Source)
Regulatory Staffing Reductions: Recent FDA staffing cuts may impact regulatory review processes, necessitating proactive compliance strategies. (Source)
Standardization Challenges: Lack of standardized data formats can hinder data integration and analysis across platforms. (Source)
Real-Time Monitoring: Implementing real-time data monitoring can significantly reduce the time to detect and address data issues. (Source)
Global Regulatory Variations: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements, complicating multinational trials.
Explore Courses for Clinical Research Career
Courses Available:
Conclusion
Effectively managing clinical trial data in 2025 requires a proactive, tech-savvy, and compliance-focused approach. From handling big data and resolving inconsistencies to navigating shifting regulations and protecting against data breaches, every aspect demands strategic planning and continuous improvement. By integrating advanced technologies, adhering to regulatory standards, and prioritizing data security, clinical research teams can maintain data integrity and drive successful outcomes. At CCRPS, we are committed to providing expert-led training and resources to help professionals confidently navigate these challenges and excel in clinical data management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The biggest challenge in 2025 is managing and integrating vast volumes of complex data from multiple sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and decentralized clinical trials. This includes ensuring data accuracy, interoperability, and real-time accessibility while maintaining compliance with global regulations.
-
Teams can use multiple imputation techniques to estimate missing data, automated validation tools to flag discrepancies, and regular audits to identify issues early. Additionally, comprehensive staff training helps prevent data entry errors that often cause inconsistencies.
-
Common tools include electronic data capture (EDC) systems, clinical trial management systems (CTMS), and cloud-based platforms like Medidata, Oracle Clinical, and Veeva Vault. These tools streamline data collection, monitoring, and analysis, improving efficiency and accuracy.
-
Each region has unique requirements:
FDA (U.S.): Follows 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records.
EMA (EU): Requires compliance with GDPR and ICH-GCP.
MHRA (UK): Follows similar standards with additional post-Brexit guidelines.
Global trials must align with all applicable standards, making regulatory monitoring essential.
-
Best practices include:
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit
Conducting regular cybersecurity audits
Training all staff on secure data handling
Creating and testing an incident response plan
These steps help ensure patient privacy and data integrity throughout the trial lifecycle.