Top 50 GCP Certification Exam Questions and Complete Answers
The GCP Certification (Good Clinical Practice) is a globally recognized standard for clinical trial conduct, ensuring that trials are ethically sound, scientifically valid, and patient-safe. This certification is crucial for professionals involved in clinical research, helping them adhere to regulatory guidelines and ethical standards that govern clinical trials. It validates an individual’s knowledge of the legal and ethical aspects of clinical research, making them a trusted professional in the field.
Achieving GCP certification opens doors to new career opportunities in clinical research, as it is recognized worldwide as a mark of competence and credibility. In this guide, we’ll cover the top 50 GCP certification exam questions, offering you a comprehensive list of essential questions and answers. Additionally, we’ll explore common challenges in the exam, effective strategies for answering tough questions, and how enrolling in a GCP certification course can significantly boost your chances of success.
Overview of GCP Certification
The GCP certification is essential for professionals working in clinical research and clinical trials, as it provides a structured framework for maintaining high standards of quality, safety, and compliance. It covers critical areas such as the ethical conduct of clinical trials, ensuring that patients' rights and safety are protected, as well as the integrity of clinical data. The certification equips candidates with the knowledge to understand regulatory requirements, including FDA guidelines and international standards like ICH-GCP.
For clinical research professionals, GCP certification is often a requirement for working with regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies. This certification assures employers that the professional is trained in Good Clinical Practice and fully understands the necessary processes for conducting clinical trials, from the planning phase to final reporting. Understanding the importance of patient safety, protocol adherence, and informed consent is vital to ensure successful trial outcomes and compliance with global regulatory frameworks.
Importance of Ethical Guidelines in Clinical Research
Ethical guidelines are at the heart of Good Clinical Practice (GCP), ensuring that clinical research is conducted with the highest standards of integrity and patient safety. Clinical trials often involve vulnerable populations, making it critical for researchers to prioritize participants' rights, privacy, and well-being. These ethical guidelines provide a clear framework for obtaining informed consent, managing adverse events, and ensuring data integrity throughout the research process.
Adhering to ethical principles also promotes public trust in clinical trials. It ensures that the findings are reliable and that researchers uphold the moral responsibility to participants, which is essential for the credibility of the study and its outcomes. Ethical guidelines also play a significant role in protecting the research organization and the individuals involved from legal risks and regulatory violations.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of GCP
Understanding the legal and regulatory frameworks that guide clinical trials is vital to conducting safe and compliant research. The GCP guidelines are built on both international and national regulations, ensuring that researchers follow consistent procedures to safeguard participants. These include informed consent protocols, adverse event reporting, and strict documentation requirements.
In addition to international standards like ICH-GCP, researchers must comply with local regulations set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the U.S. and the EMA in Europe. Compliance with these regulations ensures that clinical trials meet safety standards, protect patient rights, and maintain the integrity of trial data. Failing to adhere to legal and regulatory requirements can lead to severe penalties, including the invalidation of research findings, fines, and even criminal charges.
50 Essential GCP Exam Questions
| Question Number | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What is GCP? | Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is an international quality standard for conducting clinical trials, ensuring patient safety, data integrity, and ethical compliance. |
| 2 | Why is GCP important in clinical research? | GCP ensures that clinical trials are ethically conducted, with patient safety prioritized and data collected in a consistent, reliable, and compliant manner. |
| 3 | What are the main principles of GCP? | The main principles of GCP include ethical conduct, patient rights protection, data integrity, and compliance with regulatory requirements throughout clinical trials. |
| 4 | What is informed consent in clinical trials? | Informed consent is the process of providing potential clinical trial participants with sufficient information about the study, risks, and benefits, allowing them to make an informed decision. |
| 5 | What is the role of an investigator in a clinical trial? | The investigator is responsible for conducting the trial according to the approved protocol, ensuring participant safety, and ensuring compliance with GCP and regulatory requirements. |
| 6 | What is the purpose of a clinical trial protocol? | The clinical trial protocol outlines the study design, objectives, methodology, and patient safety measures. It serves as the blueprint for the entire trial. |
| 7 | What is an adverse drug reaction (ADR)? | An ADR is any harmful or unintended reaction to a drug that occurs at normal therapeutic doses, which may need medical attention. |
| 8 | What are serious adverse events (SAEs)? | SAEs are adverse events that result in death, hospitalization, disability, or require medical intervention. They must be reported immediately according to GCP guidelines. |
| 9 | What is pharmacovigilance? | Pharmacovigilance is the science of monitoring, detecting, assessing, and preventing adverse drug reactions to ensure drug safety during and after clinical trials. |
| 10 | What are the responsibilities of the ethics committee in clinical trials? | The ethics committee is responsible for reviewing and approving the clinical trial protocol, ensuring that the study meets ethical standards and protecting participants' rights. |
| 11 | What is the role of the sponsor in a clinical trial? | The sponsor is responsible for initiating, managing, and funding the clinical trial. They ensure compliance with GCP and provide necessary resources for the study. |
| 12 | What is the role of the clinical trial monitor? | The clinical trial monitor ensures that the clinical trial is conducted according to the protocol, GCP, and regulatory requirements. They oversee the trial's progress and patient safety. |
| 13 | What is a clinical trial report (CTR)? | A clinical trial report (CTR) is a comprehensive document that summarizes the methodology, results, and conclusions of a clinical trial, including data analysis. |
| 14 | What is the role of the Institutional Review Board (IRB)? | The IRB reviews and approves the clinical trial protocol to ensure the trial complies with ethical guidelines, focusing on participant safety and rights. |
| 15 | What is the definition of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)? | Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) refers to the regulations and practices that ensure pharmaceutical products are consistently produced and controlled to the highest standards. |
| 16 | What is the significance of blinding in clinical trials? | Blinding reduces bias by ensuring that neither the participant nor the investigator knows the treatment being administered, ensuring a more accurate evaluation of outcomes. |
| 17 | What is the difference between randomized and non-randomized trials? | Randomized trials involve randomly assigning participants to treatment groups, while non-randomized trials do not, which may introduce selection bias. |
| 18 | What is data integrity in clinical trials? | Data integrity ensures that clinical trial data is accurate, complete, and consistent, preventing errors and ensuring the validity of results. |
| 19 | What is clinical trial monitoring? | Clinical trial monitoring involves overseeing trial activities to ensure compliance with protocols, regulatory guidelines, and patient safety standards. |
| 20 | What is the importance of adverse event reporting? | Adverse event reporting is critical for tracking and managing negative effects during clinical trials. It helps identify risks, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance. |
| 21 | What is the difference between protocol amendments and protocol deviations? | Protocol amendments are approved changes to the trial design, while protocol deviations are unapproved changes that may impact data integrity. |
| 22 | What is the purpose of statistical analysis in clinical trials? | Statistical analysis helps determine the significance of results, ensuring the reliability of conclusions drawn from clinical data. |
| 23 | What is a data safety monitoring board (DSMB)? | The DSMB monitors trial data for participant safety and ensures that the trial continues only if benefits outweigh the risks. |
| 24 | What does informed consent protect in clinical trials? | Informed consent protects participants' autonomy, ensuring they understand the trial's risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw. |
| 25 | What is the significance of randomized controlled trials (RCTs)? | RCTs are considered the gold standard in clinical trials, as they minimize bias by randomly assigning participants to treatment groups. |
| 26 | How do blinded trials help reduce bias in clinical research? | Blinded trials prevent participants and researchers from knowing treatment assignments, ensuring outcomes are not influenced by expectations. |
| 27 | What is the importance of eligibility criteria in clinical trials? | Eligibility criteria define the specific characteristics required for participation, ensuring the trial results are applicable to the target population. |
| 28 | What is the role of data collection forms in GCP compliance? | Data collection forms ensure that clinical trial data is accurately recorded, compliant with GCP standards, and retrievable for future audits. |
| 29 | What is source data verification (SDV)? | SDV is the process of checking that clinical trial data matches original source documents to ensure accuracy and consistency. |
| 30 | What is the role of clinical trial documentation in GCP? | Clinical trial documentation ensures compliance with GCP standards, provides a record of the trial's progress, and facilitates audits and inspections. |
| 31 | What is the difference between a serious adverse event (SAE) and a non-serious adverse event? | SAEs are life-threatening or result in significant medical intervention, while non-serious adverse events do not pose immediate danger to the patient. |
| 32 | What is clinical trial monitoring? | Clinical trial monitoring involves overseeing the trial’s compliance with protocols, GCP, and regulatory standards to ensure data integrity and patient safety. |
| 33 | What is the role of the Institutional Review Board (IRB) in clinical trials? | The IRB reviews and approves the clinical trial protocol to ensure the trial complies with ethical guidelines, focusing on participant safety and rights. |
| 34 | What is Good Laboratory Practice (GLP)? | GLP is a set of principles that ensures the quality, integrity, and consistency of laboratory studies related to clinical research. |
| 35 | What is clinical trial data management (CTDM)? | CTDM is the process of collecting, cleaning, and managing data generated during clinical trials, ensuring accuracy and integrity. |
| 36 | What is the significance of the study monitor in clinical trials? | The study monitor oversees the clinical trial, ensuring compliance with GCP, tracking participant safety, and reviewing data accuracy. |
| 37 | What is the trial master file (TMF) in clinical research? | The TMF is a collection of essential trial documents, including protocols, ethics approvals, and patient consent forms, used for regulatory compliance and auditing. |
| 38 | What is the purpose of post-marketing surveillance? | Post-marketing surveillance monitors the safety of a drug after it has been released to the market, detecting long-term side effects and ADRs. |
| 39 | What is the informed consent form (ICF)? | The ICF is a document that provides potential trial participants with information about the trial, ensuring they voluntarily agree to participate. |
| 40 | What is the role of the regulatory agency in clinical trials? | Regulatory agencies like the FDA or EMA oversee the approval of clinical trials, ensuring that they meet ethical and safety standards before participants are enrolled. |
| 41 | What is Good Laboratory Practice (GLP)? | GLP is a set of principles that ensures the quality, integrity, and consistency of laboratory studies related to clinical research. |
| 42 | What is clinical trial data management (CTDM)? | CTDM is the process of collecting, cleaning, and managing data generated during clinical trials, ensuring accuracy and integrity. |
| 43 | What is the role of a clinical research associate (CRA)? | A CRA is responsible for monitoring the clinical trial’s progress, ensuring adherence to the protocol, and reporting any deviations or issues. |
| 44 | What is data validation in clinical trials? | Data validation ensures that trial data is accurate, complete, and consistent, verifying that the results reflect the true outcomes of the study. |
| 45 | What is the significance of monitoring adverse events in clinical trials? | Monitoring adverse events ensures patient safety by detecting any harmful reactions to the drug, enabling timely interventions and reporting to regulatory bodies. |
| 46 | What is source data verification (SDV)? | SDV is the process of checking that clinical trial data matches original source documents to ensure accuracy and consistency. |
| 47 | What is the trial master file (TMF)? | The TMF contains essential documents for the trial, ensuring GCP compliance and assisting in audits and regulatory inspections. |
| 48 | What is the role of an investigator in a clinical trial? | The investigator is responsible for conducting the trial according to the approved protocol, ensuring patient safety, and ensuring compliance with GCP and regulatory requirements. |
| 49 | What is randomization in clinical trials? | Randomization is the process of assigning participants to different treatment groups in a random manner, ensuring unbiased results. |
| 50 | What is the importance of blinding in clinical research? | Blinding ensures that neither the participants nor the investigators know who is receiving which treatment, reducing bias in the trial's outcomes. |
Common Challenges in GCP Certification Exam
The GCP Certification Exam can be challenging due to the depth of knowledge required and the complexity of the clinical trial scenarios you may encounter. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common challenges that candidates face when preparing for the exam and provide strategies to overcome them.
Time Management During the Exam
One of the most significant challenges during the GCP Certification Exam is managing your time effectively. The exam covers a broad range of topics, including adverse drug reactions (ADRs), clinical trial protocols, regulatory compliance, and ethical guidelines. With a limited time frame to answer all the questions, it is essential to pace yourself carefully.
Strategies to manage your time effectively:
Prioritize easier questions: Start with questions you are most confident about to secure quick points before moving on to more difficult ones.
Don’t linger too long on one question: If you’re stuck on a question, move on and come back to it later if time permits.
Practice time management: In your preparation, take practice exams under timed conditions to get used to answering questions quickly.
Understanding Complex Scenarios in Clinical Trials
Another challenge is understanding complex clinical trial scenarios. The GCP exam often includes case studies or scenario-based questions that test your ability to apply ethical guidelines and regulatory standards in real-world situations. These questions may involve risk management, informed consent, and adverse event reporting, requiring you to think critically and make decisions based on regulatory compliance and patient safety.
Tips for handling complex scenarios:
Study real-world case studies: Review actual clinical trial scenarios to understand how GCP principles are applied in practice.
Understand regulatory guidelines: Focus on understanding the guidelines from agencies like the FDA, EMA, and ICH.
Develop decision-making skills: Practice applying ethical principles to various situations, making informed decisions that prioritize patient safety and trial integrity.
| Challenge | Solution/Strategy | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Practice with timed exams to improve your ability to pace yourself. | Time management is essential to completing the exam within the allotted time. Take practice exams under time constraints to ensure you can answer questions efficiently. Learn to allocate time for each section based on its difficulty level. |
| Complex Scenarios | Study real-world case studies to improve decision-making skills. | GCP exams often present complex clinical trial scenarios that require critical thinking and application of GCP guidelines. Studying real-world examples will help you understand how to approach these scenarios logically and ethically. |
| Regulatory Knowledge | Stay up-to-date with changes in global regulations and guidelines. | As GCP and clinical trial regulations constantly evolve, it’s crucial to remain informed on global guidelines from agencies like the FDA, EMA, and WHO. Regularly review updates and changes to stay prepared for exam questions on regulatory compliance. |
How to Tackle Difficult Questions on the GCP Exam
The GCP Certification Exam can sometimes present particularly difficult questions, especially those that involve interpreting complex clinical trial scenarios or understanding intricate regulatory frameworks. This section will explore strategies for tackling these challenging questions during the exam.
Strategies for Overcoming Tough Questions
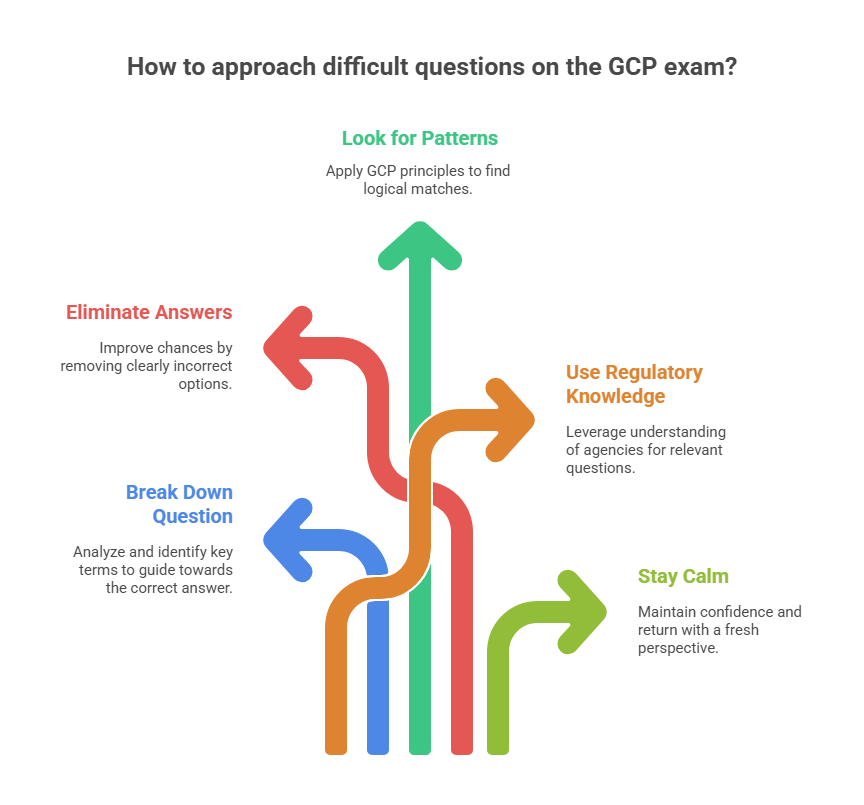
Break Down the Question
Start by breaking down the question into smaller, manageable parts. Look for keywords and phrases that can guide you toward the correct answer. Often, the question will contain hints that point to the most relevant regulatory guidelines or GCP principles.Eliminate Clearly Incorrect Answers
If the question is multiple-choice, start by eliminating answers that are clearly wrong. This will improve your chances of selecting the correct answer, even if you're unsure. Reducing the pool of choices can often give you a clearer idea of which response is most accurate.Look for Logical Patterns
Many questions in the GCP exam are designed to test your practical knowledge of real-world clinical trial situations. Think about how GCP principles apply in the real world and look for patterns in the answer choices that align with regulatory standards and ethical guidelines.Use Your Knowledge of Regulatory Bodies
When you encounter complex regulatory questions, remember that regulatory agencies like the FDA, EMA, and WHO all have guidelines that often overlap in their requirements. Use your understanding of these guidelines to guide you to the correct answer, especially when the question involves patient safety or data integrity.Take a Deep Breath and Stay Calm
Anxiety can negatively affect your performance. Stay calm, take deep breaths, and approach each question methodically. If you encounter a particularly tough question, don’t let it affect your focus. Move on to the next question and return to it later with a fresh perspective.
How Our GCP Certification Course Helps You Prepare for the Exam
Enrolling in our GCP certification course is one of the most effective ways to ensure you’re fully prepared for the GCP Certification Exam. This course is specifically designed to equip you with the essential knowledge and skills to excel in the exam and apply Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards effectively in clinical research.
Why Our GCP Certification Course is Crucial for Your Exam Success
Comprehensive Curriculum
Our course offers a complete curriculum that covers all areas critical to passing the GCP exam. From ethical guidelines to clinical trial protocols, and regulatory compliance, the course ensures you understand all aspects of GCP.Expert-Led Instruction
Learn directly from experienced professionals who bring practical knowledge of clinical trials, adverse event reporting, and regulatory requirements. Their expertise and real-world experience are invaluable as they guide you through the course material.Tailored Exam Preparation
Our GCP certification course includes practice exams, study resources, and exam-specific strategies designed to familiarize you with the types of questions you’ll face, improving your ability to tackle the exam confidently.Flexible Learning Options
We offer online, in-person, and hybrid learning formats to accommodate your schedule and learning preferences. You can study at your own pace, ensuring you have ample time to review materials and absorb key concepts.Boosted Confidence
Completing our GCP certification course will give you the confidence you need to succeed. You’ll be thoroughly prepared for the exam, and equipped with the expertise to apply GCP principles in real-world clinical research scenarios.
By enrolling in our GCP Certification Course, you’ll not only prepare for the exam but also gain the confidence and practical skills needed to advance in your career in clinical research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The GCP certification exam is an assessment designed to evaluate your knowledge of Good Clinical Practice guidelines, ethical standards, regulatory requirements, and clinical trial management. Passing this exam demonstrates your competency in ensuring patient safety, regulatory compliance, and data integrity in clinical trials.
-
Obtaining the GCP certification opens up career opportunities in clinical research, drug safety, and regulatory affairs. It validates your understanding of key principles and regulatory standards, which are essential for working in clinical trials and ensures that you are compliant with industry standards.
-
To prepare for the GCP certification exam, study the GCP guidelines and understand clinical trial protocols, adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and ethical guidelines. Enrolling in a GCP certification course can provide a structured approach to studying and offer valuable practice questions.
-
The exam typically covers topics such as ethical guidelines, adverse event reporting, clinical trial management, regulatory requirements, and informed consent. Understanding these areas and how they apply to real-world clinical trials is crucial to succeeding in the exam.
-
The passing score for the GCP certification exam usually ranges between 70% and 80%, depending on the certifying organization. It’s important to check the specific requirements of the certification provider to confirm the exact passing criteria.
-
Preparation time varies depending on your background. On average, candidates spend about 4-6 weeks preparing for the GCP certification exam. This includes reviewing study materials, completing practice exams, and understanding the application of GCP guidelines in clinical trials.
-
Most GCP certifications are valid for 2-3 years. After this period, you may need to complete continuing education or recertification to maintain your certification status. Check with your certification provider for specific renewal requirements.
Conclusion: Passing the GCP Exam with Confidence
Successfully passing the GCP Certification Exam is a major achievement that validates your expertise in conducting ethical and compliant clinical trials. By mastering the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, you not only enhance your career opportunities in clinical research and drug safety but also contribute to the safety and well-being of patients in clinical trials.
The exam may be challenging, but with thorough preparation, a structured study plan, and the right resources, you can approach it with confidence. Enrolling in a GCP certification course provides the necessary tools to help you succeed, offering expert-led instruction, practice exams, and a deep dive into the essential topics covered in the certification exam.
Keep in mind that the skills you gain from this certification will serve you beyond the exam, positioning you as a trusted professional in the field of clinical research. With the right preparation and commitment, you’ll be ready to pass the exam and take the next step in advancing your career.
Thank you for participating!