Introduction to Pharmacovigilance
Fig 1: Drug safety and pharmacovigilance
Introduction to pharmacovigilance
As stated by World Health Organization, ”Pharmacovigilance also known as drug safety, is the pharmacological science that deals with the activities of signal detection, evaluation, and prevention of adverse drug reactions associated with the use of medicines”.
Aims of pharmacy vigilance are the following
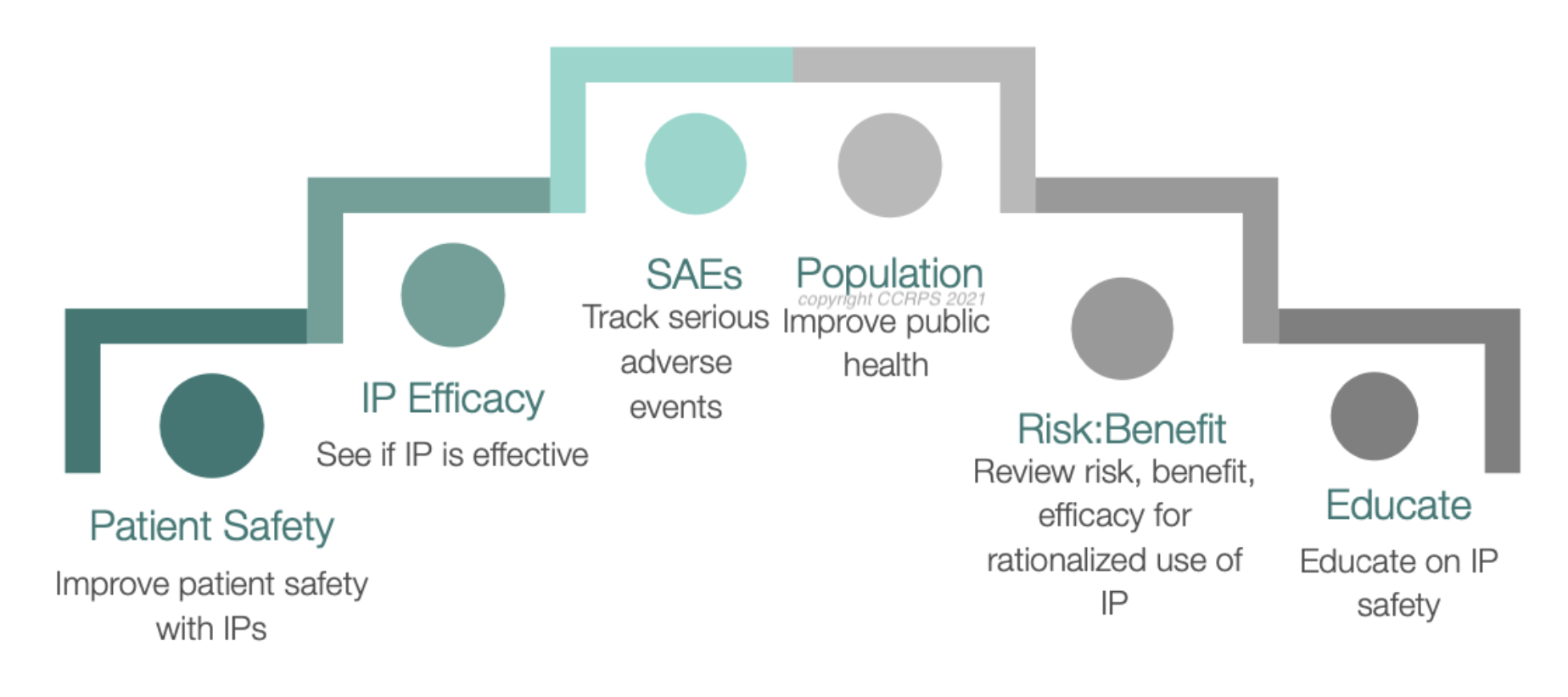
Fig 2: why do we need pharmacovigilance
• Improve patient care about the drugs and keep the patient safe from adverse effects of drug
• To ensure the safety of a drug, it is essential to implement pharmacovigilance, which monitors even rare and severe adverse effects. This step is not only necessary for new drugs but also for those that are well-established. Furthermore, training should focus on both the general population and healthcare professionals, as early detection and reporting are critical for patient safety.
• To research the efficacy of the drug and check effects of drugs during trials to the pharmacy and then keep monitoring their effects for many years. To research the efficacy of the drug and check effects of drugs during trials to the pharmacy and then keep monitoring their effects for many years
• To improve the current state of the public healthcare system, a complete evaluation of the effect of drugs on the body should be performed.
• Promote training and knowledge about this field of medicine
• To know the mechanisms of the drug inside the human body
• To encourage safe and rational use of medicines
Objectives of pharmacovigilance
• To properly detect the unknown adverse effect and drug interaction
• Distribution of information about the adverse effect of drugs and drug interactions so that they occur less frequently
• Timely correction of therapeutic errors
• Reevaluation of the risk-benefit balance of medicine, so we can effectively use those drugs for a patient having more benefits and fewer side effects
• Identifications of mechanisms that cause adverse effects of drugs
Fig 3: Stakeholders in pharmacovigilance
There are mainly four stake holders in pharmacovigilance
1- Patient
2- Doctor or pharmacist
3- Marketing authorization holder
4- Regulators such as authorities, committee
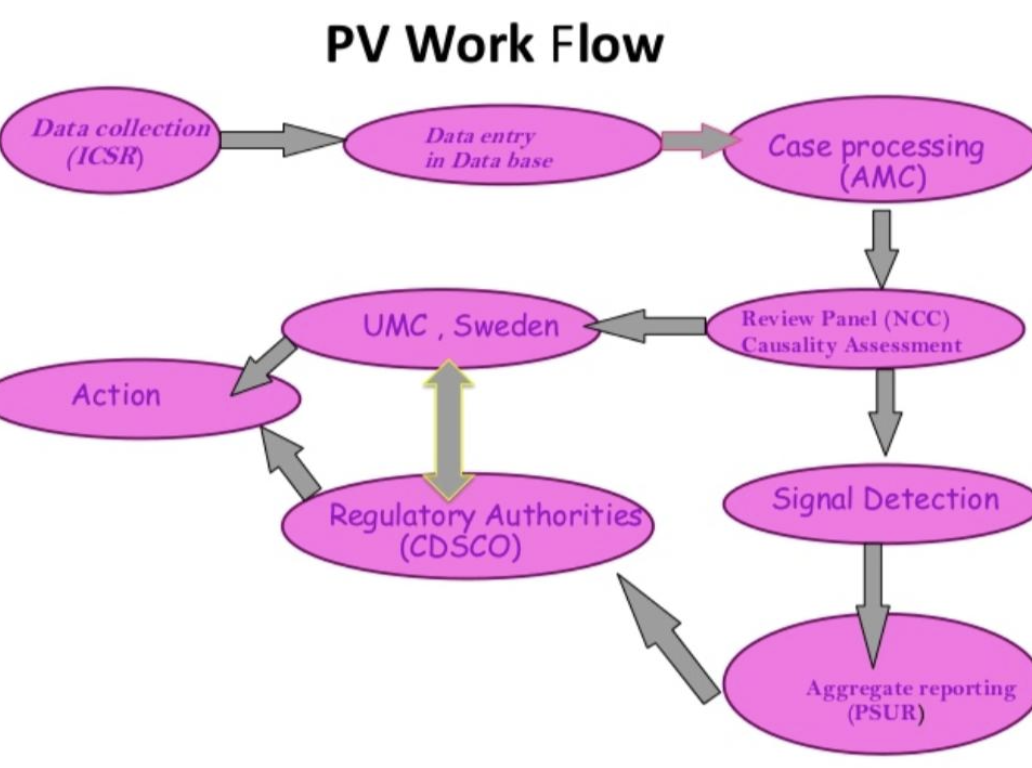
Steps of pharmacovigilance
Step 1 is the collection of reports about the adverse effect and all adverse reactions of the drugs. All adverse reactions, including serious and unexpected effects, are subjected to expedited reporting.
Step 2 involves receiving the cumulative reports regarding the safety of drugs and sending those reports to all the regulatory authorities.
Step 3 The process of determining the specific adverse effect associated with a specified drug and then comparing this drug with another drug having a similar worse effect.
Step 4 Management of adverse effects of the drugs. Receive information regarding the harmful effects on patients or population and seek a method to minimize these effects.
Pharmacovigilance regulations:
International Conference of Harmonization consists of authorities from India, Europe, and Japan with representatives of the correlating industries, health organization, and WHO as an observer. This conference provides guidelines regarding pharmacovigilance and good drugs. There is stepwise development of instructions. At step four, there is a consensus internationally, and at step 5, an agreement for regulators to introduce the guidelines to legislation.
The principal role of pharmacovigilance is to ensure the safer usage of drugs. But the pressure is increasing on this field to analyze data about the adverse effect, monitor risk more broadly, and accurately reports patient events.
What information should we report to higher authorities?
• Any information on adverse drug reaction
• lack of efficacy of the drug
• Even when there is no observed adverse effect, report abuse of the drug, effect of overdose, and about drug administration during pregnancy
Free resources for introduction to pharmacovigilance:
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/2020/04/11/introduction-to-pharmacovigilance/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/for-experienced/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/2020/04/11/pharmacovigilance-regulations/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/2020/04/20/sources-of-adr-collections-and-reporting-forms/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/2020/04/26/icsr-processing-tools/
https://pharmacovigilancetutorials.wordpress.com/2020/04/26/signal-detection-and-management/





What Is Pharmacovigilance? - Definition, Jobs, Salary, And Pharmacovigilance Certification:
A Guide All About Pharmacovigilance