Clinical Study Coordinator Training Program
A study coordinator is the backbone of any research project. They are responsible for ensuring that all the elements of the study further the goals of the study, or the research objective. A study coordinator’s foresight and attention to detail are critical to the success of every trial.
Role Of A Study Coordinator
The role of a study coordinator is broad and includes the following:
In the planning stage: ensure that the plan is comprehensive enough to cover all aspects of the study and that various processes and elements of the study are linked. For those looking to become a study coordinator, the Clinical Research Coordinator course can provide essential training.
At the time of execution: ensure the availability of funds, apparatus, infrastructure, etc. required for the study. Further, they also have to ensure that the study flows promptly. Knowledge of ICH-GCP standards, covered in our certification course, is crucial here.
When various elements of the study are near to completion: the study coordinator will have the role to align them in a planned manner.
At all stages for research: a study coordinator ensures that research ethics are maintained, and there is no violation of any code of conduct.
Determine the Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) to be followed in a study. The Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification can help develop the skills needed to define and manage SOPs effectively.
Work opportunities for a study coordinator
In many countries, such as India, study coordinators are a relatively new career route and hence acutely unexplored. However, considering the growth in research and development areas, it is pretty evident that there is an increasing demand for them. Presently, the industry needs study coordinators while only a handful of them exist.
Due to this demand-supply gap, the monetary compensation of such positions has been very high. Research by Salary.com contends that the median salary of a clinical research coordinator is around $63,330. However, based on the type of study, the range may vary from as low as $2,000 per month to as high as $4,500 per month. Those interested in expanding their career options might consider training as a Clinical Trials Assistant, or specialize further with the Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification or Medical Monitor Certification.
Importance
Every field of work needs consistent education, and there's always a scope for enhancement. The area of work of a study coordinator is no exception. The sky is the limit, and each training program is a step towards reaching perfection.
A study coordinator training program focuses on developing individuals to perform the roles mentioned above, in addition to other roles that may be expected from a study coordinator.
For example, regulations and code of ethics governing the respective field of study may also get updated from time to time. In such cases, it becomes necessary for the coordinators to obtain a basic understanding of the changes and implement them in a study.
Moreover, certain organizations may require applicants to have taken certain training courses before considering them for a position. Thus, it has become evermore important for hopeful professionals to take the right training courses.
Who Will Provide The Training?
Depending on the area of study, various institutions, or people with immense experience in the relevant field may provide training.
For example, an organization may organise EA training for its employees from experts in the industry. Other examples of are specialized training courses for coordinators, such as the Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC) training provided by the CITI Program.
Further, various universities run comprehensive and dedicated courses for imparting study coordinator training. Some such institutes are Clinical and Translational Science Institute (CTSI), which provides basic coordinator training, and ACRP, which provides Certified Clinical Research Coordinator (CCRC) training.
Conclusion
The field of a study coordinator is a career that has immense potential yet to be explored. More trained professionals can prove to be very valuable assets to the research processes. At CCRPS, we offer ACCRE accredited training specialized for study coordinators. In addition, we have complied articles below to help you better understand the complex aspects of clinical research.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
How to Save Money on Becoming a Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC)
If you think practically, then you will find that nothing in this world comes for free. But if you have a passion for clinical research and need to learn on a budget, here are some ways you can enhance your understanding without breaking the bank.
To understand how you can learn for free, it’s first important to understand the typical trajectory of a clinical research coordinator:
A person seeking clinical research coordinator training should complete high school. There they learn must-have all the science subjects like physics, chemistry, and biology.
After high school, institutes for professional clinical research coordinator professionalism offer programs that are essential for later.
In addition, one can get an experience graduate certificate from an online source. This would help the person reach their career goals faster.
Alternatively, they can complete a bachelor's degree of science.
After completing the bachelor's degree, a master's degree is needed for some of the higher pay-grade positions.
How to get free clinical research coordinator training?
If looking at the education requirements for a clinical research coordinator makes you dizzy, you’re not alone. Becoming a clinical research coordinator takes a lot of time and money. That is why many students turn to scholarships and healthcare programs to help pay their tuition.
On the other hand, there are many websites that offer free or affordable information and training for aspiring professionals. While they can’t replace a formal education, they can supplement your resume and knowledge. While some important topics include clinical data management, pharmacovigilance, and regulatory authorities, you should strive for a comprehensive understanding of the field. At CCRPS, we offer affordable courses designed for clinical research coordinators as well as free ICH GCP training. These can help you build your resume and land the position you want.
In addition, it is really important to keep updated with new clinical research headlines. Below, I have complied some articles that aspiring professionals might find useful. The best thing you can do for your education is to start now and not later.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
How to Make a Career out of Clinical Research Management (CRC)?
A clinical research coordinator or CRC is a highly trained professional, whose expertise is crucial to all medical research work. Although a CRC works under the constant guidance of a principal investigator, they are responsible for the day to day trials and clinical operations. Thus, this profession can be quite challenging but rewarding.
However, getting into the crew of CRCs is not an easy task. A particular individual may need to prepare for a while to be selected for such a post. In this segment, you can learn all the aspects to becoming a successful CRC.
What does a Clinical Research Coordinator do?
A clinical research coordinator or CRC is a highly trained professional, whose expertise is crucial to all medical research work. Although a CRC works under the constant guidance of a principal investigator, they are responsible for the day-to-day trials and clinical operations. Thus, this profession can be quite challenging but rewarding.
However, getting into the crew of CRCs is not an easy task. A particular individual may need to prepare for a while to be selected for such a post. In this segment, you can learn all the aspects to becoming a successful CRC through specialized training such as the Clinical Research Coordinator course.
What does a Clinical Research Coordinator do?
The field of medicine is always advancing. In the world of medicine, new knowledge is indispensable. So, the professionals of the medical branch are always looking to conducting experiments that can lead them to new cures and successes. Among clinical research professionals, clinical research coordinators are at the front lines of research operations and analytics.
The duties of a CRC are to plan and initiate a study or experiment the board has approved. During the phases of the project, they must maintain communication between their site and institutional organizations. The CRCs are eligible to do the research and reviews. Additionally, they can choose to hire potent candidates for their purpose. Understanding and adherence to ICH-GCP guidelines are crucial for ensuring compliance and ethical conduct in their studies.
How can you be a successful clinical research coordinator?
The job of a clinical research coordinator is not an easy one. However, with enough hard work and patience, one can become eligible for the post. Although, individuals who aspire to become a clinical research coordinator are advised to understand the basics and keep educating themselves if they want to become a trusted professional. Continual education and certification, such as the Pharmacovigilance Certification and Clinical Trials Assistant Training, can provide essential knowledge and skills required in this evolving field.
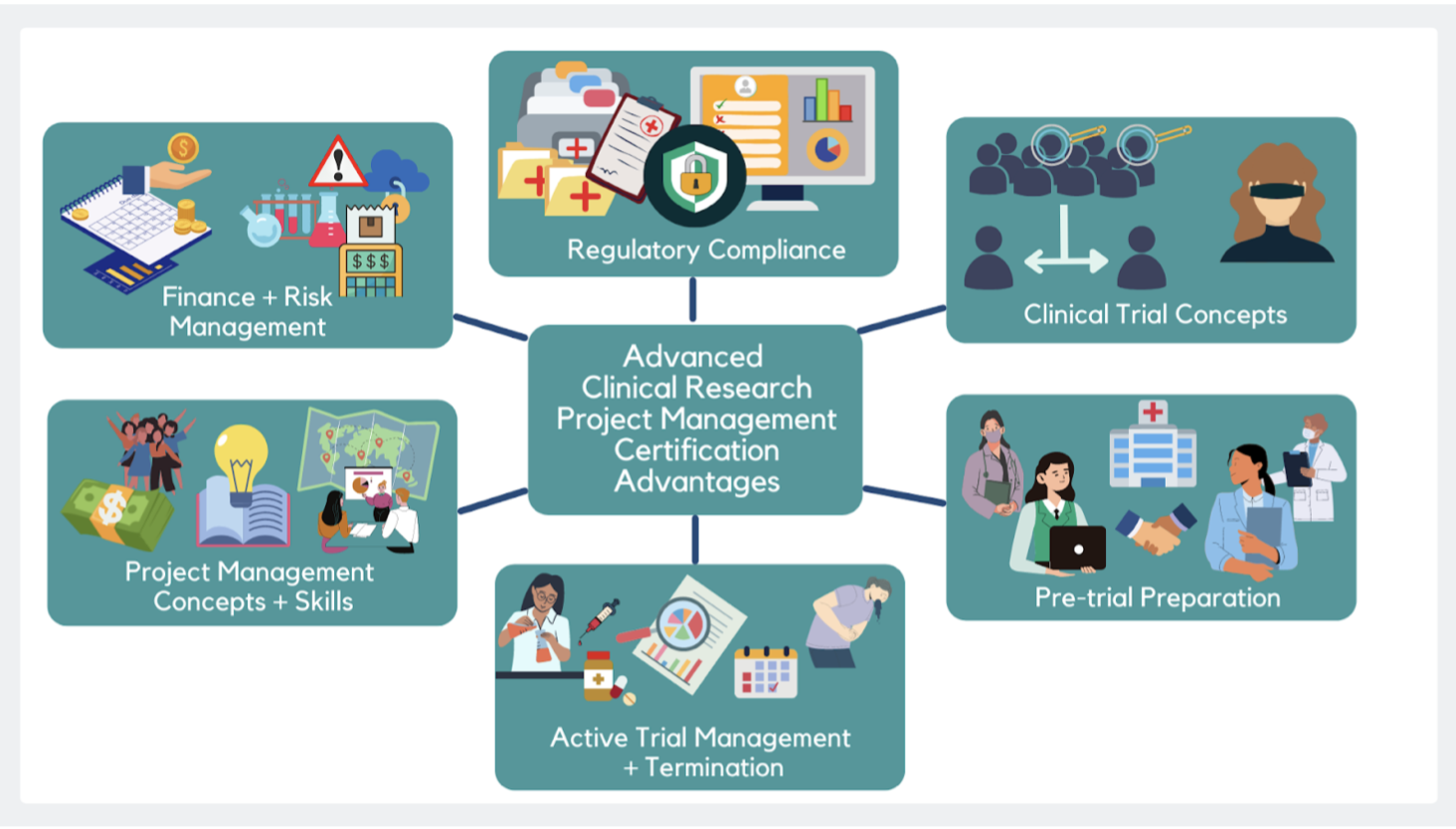
Additionally, for those looking to further their careers, the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification are excellent resources to consider. Those interested in overseeing clinical trials and research safety might consider the Medical Monitor Certification.
Here are the requirements to become a successful clinical research coordinator:
1. To apply for this post and profession, the candidates need to have a background that is related to the field of medicine or biology. The general preference for applying is to have a bachelor's degree in microbiology or medical technology.
2. Some positions require individuals who have a master’s degree on top of their bachelor’s degree. So, you might need to invest more time into your education if you want to work with certain firms or reach a higher pay-grade.
3. Preparing yourself for the job is crucial. As this job is a challenging one, individuals might need to develop and train themselves for quite some time to do well. For young training candidates, clinical trial coordinator training is shown to be quite a useful resource. At CCRPS, we offer affordable training courses developed by real professionals and accredited by ACCRE. If you are looking to learn more about clinical research and specific positions, CCRPS can be the perfect starting point.
A step towards the development of humankind
Medical science has experienced great expeditions over the past few decades, and all of that has help benefit society in some way or the other. Thus, becoming a part of a research team is a commendable task indeed.
Becoming a clinical research coordinator isn’t easy. A CRC must have an eye for detail and need to continually polish their skills. Moreover, experience and education is a determining quality that can set a good CRC apart from the rest in the lot. If you’d like to start your education, check out CCRPS. Our courses and articles will help you find the tools to succeed in clinical research.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
Clinical Research Coordinator Classes
A Guide to Clinical Research Coordinator Classes
The medical field thrives on constant innovation. From uncovering new treatments to battling life-threatening illnesses, there's a relentless need for fresh talent. One crucial role at the forefront of medical discovery is the clinical research coordinator (CRC).
Who is a Clinical Research Coordinator?
A CRC, sometimes called a site research coordinator, study coordinator, or simply CRC, is the backbone of a research site. You'll possess a deep understanding of research guidelines, clinical processes, and more. Your responsibilities include documentation, subject well-being, and conducting research procedures. To develop a foundational understanding, consider enrolling in a Clinical Research Coordinator course.
What Does a Clinical Research Coordinator Do?
A CRC's role requires meticulous attention to detail and unwavering precision. CRCs are guided by a principal investigator (PI), who oversees the entire research project's proper execution.
The studies CRCs undertake are often complex, requiring days or even months of analysis. Patience and focus are essential qualities. Moreover, as a representative of your medical institution, PI, and colleagues, building strong relationships with other professionals is paramount.
Building a Fulfilling Career as a CRC
There's no single educational path to becoming a CRC. A background in pharmacy, nursing, business administration, statistics, biology, teaching, health record maintenance, or even medical technology can pave the way. CRCs find employment in research groups, private institutions, pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and more.
The Skills and Knowledge of a Successful CRC
Clinical research demands accuracy. Refining your skills is crucial for success. Here's what you can leverage when applying for CRC positions:
Educational Background: A bachelor's degree in microbiology or medical technology is ideal. However, relevant experience and coursework can strengthen your application. Employers value what you bring to the table, not what you lack.
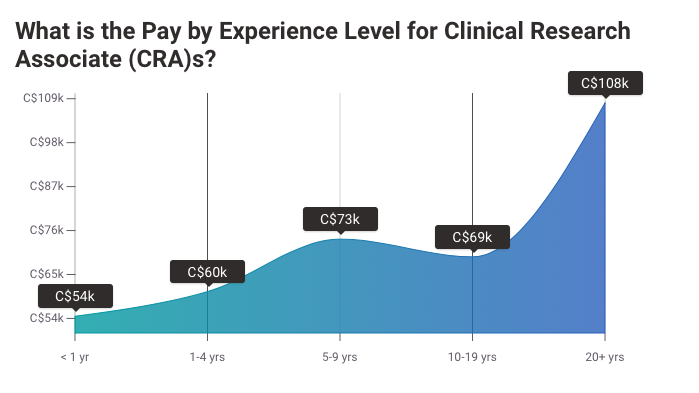
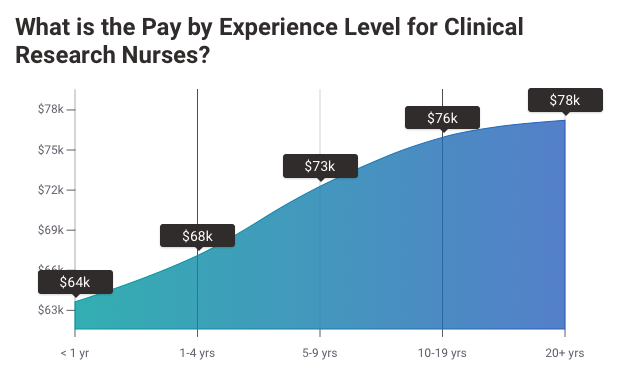
Experience: Entry-level positions often seek candidates with 1-2 years of experience, while senior roles might require 5-6 years. Master's degrees can be advantageous for higher-level positions with better pay.
Enhancing Your Qualifications: Clinical Research Coordinator Classes
Formal education through clinical research coordinator classes can significantly enhance your qualifications. These programs equip you with the specific knowledge and practical skills required to excel in this dynamic field. Here are the different types of CRC classes available:
Certificate Programs: These intensive programs offer a comprehensive foundation in clinical research principles, regulations, and best practices. They typically last several months and can be completed online or in-person. For those interested in gaining specialized knowledge, exploring a Pharmacovigilance Certification or ICH-GCP course can be highly beneficial.
Associate's Degree Programs: For those seeking a more in-depth education, associate's degree programs delve deeper into research methodology, data management, and ethical considerations. They can take up to two years to complete. Aspiring research coordinators may also consider a Clinical Trials Assistant Training program to further enhance their practical skills.
Bachelor's Degree Programs: A bachelor's degree in clinical research provides the most thorough education. These programs equip you with advanced research skills, project management expertise, and a strong understanding of research ethics. Earning a bachelor's degree can take four years or more.
Benefits of Taking Clinical Research Coordinator Classes
Investing in CRC classes offers several advantages:
Stronger Job Prospects: Formal education demonstrates your commitment to the field and equips you with the knowledge and skills employers seek.
Enhanced Skills and Knowledge: You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of research protocols, data collection, regulatory compliance, and ethical considerations.
Career Advancement: Formal education can open doors to senior-level positions and better career opportunities.
Networking Opportunities: Many programs offer opportunities to connect with instructors and fellow students, building a valuable professional network.
For those aiming at leadership roles or seeking to further specialize, consider advanced certifications such as the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification or the Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification. Additionally, a Medical Monitor Certification can prepare you for critical oversight roles within clinical trials.
Finding the Right Clinical Research Coordinator Class
When choosing a CRC class, consider these factors:
Accreditation: Ensure the program is accredited by a reputable organization.
Course Curriculum: Evaluate if the curriculum aligns with your career goals and covers essential topics like research ethics, Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and regulatory requirements.
Delivery Format: Choose between online, in-person, or blended learning options to suit your learning style and schedule.
Cost and Time Commitment: Consider the program's cost and how long it will take to complete.
Conclusion
A career as a clinical research coordinator is a rewarding opportunity to contribute to medical advancements. By taking advantage of clinical research coordinator classes, you can gain the knowledge and skills to thrive in this dynamic and growing field. With dedication and the right education, you can launch a fulfilling career at the forefront of medical discovery.
Additional Tips
Research professional organizations: Explore resources offered by organizations like the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP) for career guidance and educational opportunities.
Volunteer in research settings: Gain valuable practical experience by volunteering for research studies or clinical trials.
Develop transferable skills: Hone your communication, interpersonal, and organizational skills.
Feel free to check out our courses and some of our other articles in the slider below.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
COVID-19 Summary of 102 Clinical Trials
All trial information below is sourced from the clinicaltrials.gov website.
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF HUAI ER IN THE ADJUVANT TREATMENT OF COVID-19
Drug: Huaier Granule
Mortality rate|Clinical status assessed according to the official guideline|The differences in oxygen intake methods|Duration (days) of supplemental oxygenation|Duration (days) of mechanical ventilation|The mean PaO2/FiO2|Length of hospital stay (days)|Length of ICU stay (days)|Pulmonary function
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
N=550
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
April 1, 2020 - September 1, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04291053
RECOMBINANT HUMAN ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME 2 (RHACE2) AS A TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH COVID-19
Drug: Recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (rhACE2)
Time course of body temperature (fever)|Viral load over time|P/F ratio over time|Sequential organ failure assessment score(SOFA score) over time|Pulmonary Severity Index (PSI)|Image examination of chest over time|Proportion of subjects who progressed to critical illness or death|Time from first dose to conversion to normal or mild pneumonia|T-lymphocyte counts over time|C-reactive protein levels over time|Angiotensin II (Ang II) changes over time|Angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) changes over time|Angiotensin 1-5 (Ang 1-5) changes over time|Renin changes over time|Aldosterone changes over time|Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) changes over time|Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) changes over time|Interleukin 6 (IL-6) changes over time|Interleukin 8 (IL-8) changes over time|Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor type II (sTNFrII) changes over time|Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) changes over time|Von willebrand factor (vWF) changes over time|Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) changes over time|Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) changes over time|Surfactant protein-D (SP-D) changes over time|Angiopoietin-2 changes over time|Frequency of adverse events and severe adverse events
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
N=0
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 2020 - April 2020
GCP Office of The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04287686
CLINICAL TRIAL ON REGULARITY OF TCM SYNDROME AND DIFFERENTIATION TREATMENT OF COVID-19.
Drug: TCM prescriptions
The relief / disappearance rate of main symptoms|Chest CT absorption|Virus antigen negative conversion rate|Clinical effective time: the average effective time|The number of severe and critical conversion cases|Incidence of complications|Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Score
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
N=340
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
March 2, 2020-May 2020
Huai'an fourth people's Hospital, Huaian, Jiangsu, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04306497
THE COVID-19 MOBILE HEALTH STUDY (CMHS)
Other: nCapp, a cell phone-based auto-diagnosis system
Accuracy of nCapp COVID-19 risk diagnostic model
18 Years to 90 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
N=450
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 14, 2020-May 31, 2020
Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04275947
A PILOT STUDY OF SILDENAFIL IN COVID-19
Drug: Sildenafil citrate tablets
Rate of disease remission|Rate of entering the critical stage|Time of entering the critical stage|Rate of no fever|Rate of respiratory symptom remission|Rate of lung imaging recovery|Rate of C-reactive protein (CRP) recovery|Rate of Biochemical criterion (CK, ALT, Mb) recovery|Rate of undetectable viral RNA (continuous twice)|Time for hospitalization|Rate of adverse event
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
N=10
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 9, 2020-November 9, 2020
Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04304313
Key Clinical Trials in COVID-19 Treatment and Intervention Strategies
Relevant Courses for Understanding Clinical Trials:
This list of courses offers comprehensive training and certification opportunities for professionals interested in enhancing their understanding and skills in clinical research, particularly in navigating the complexities of COVID-19 clinical trials.
CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 IN HONG KONG: A MULTICENTRE OBSERVATIONAL COHORT STUDY
28 day mortality|vasopressor days|days on mechanical ventilation|sequential organ function assessment score|ECMO use|percentage nitric oxide use|percentage free from oxygen supplement
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
N=8
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Retrospective
February 14, 2020-February 25, 2020
Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04285801
SAFETY AND IMMUNITY OF COVID-19 AAPC VACCINE
Biological: Pathogen-specific aAPC
Frequency of vaccine events|Frequency of serious vaccine events|Proportion of subjects with positive T cell response|28-day mortality|Duration of mechanical ventilation if applicable|Proportion of patients in each category of the 7-point scale|Proportion of patients with normalized inflammation factors|Clinical improvement based on the 7-point scale if applicable|Lower Murray lung injury score if applicable
6 Months to 80 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1
N=100
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 15, 2020-December 31, 2024
Shenzhen Geno-immune Medical Institute, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04299724
TREATMENT OF MILD CASES AND CHEMOPROPHYLAXIS OF CONTACTS AS PREVENTION OF THE COVID-19 EPIDEMIC
Drug: Antiviral treatment and prophylaxis|Other: Standard Public Health measures
Effectiveness of chemoprophylaxis assessed by incidence of secondary COVID-19 cases|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at days 3|The mortality rate of subjects at weeks 2|Proportion of participants that drop out of study|Proportion of participants that show non-compliance with study drug
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
N= 3040
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
March 15, 2020-July 15, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04304053
COMPARISON OF LOPINAVIR/RITONAVIR OR HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE IN PATIENTS WITH MILD CORONAVIRUS DISEASE (COVID-19)
Drug: Lopinavir/ritonavir|Drug: Hydroxychloroquine sulfate
Viral load|Viral load change|Time to clinical improvement (TTCI)|Percentage of progression to supplemental oxygen requirement by day 7|Time to NEWS2 (National Early Warning Score 2) of 3 or more maintained for 24 hours by day 7|Time to clinical failure, defined as the time to death, mechanical ventilation, or ICU admission|Rate of switch to Lopinavir/ritonavir or hydroxychloroquine by day 7|adverse effects|Concentration of Lopinavir/ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine
16 Years to 99 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
N=150
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 11, 2020-May 2020
Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04307693
STUDY TO EVALUATE THE SAFETY AND ANTIVIRAL ACTIVITY OF REMDESIVIR (GS-5734™) IN PARTICIPANTS WITH SEVERE CORONAVIRUS DISEASE (COVID-19)
Drug: Remdesivir|Drug: Standard of Care
Proportion of Participants With Normalization of Fever and Oxygen Saturation Through Day 14|Proportion of Participants With Treatment Emergent Adverse Events Leading to Study Drug Discontinuation
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
N=400
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 6, 2020-May 2020
Providence Regional Medical Center Everett, Everett, Washington, United States|Swedish Center for Comprehensive Care, Seattle, Washington, United States|Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea, Republic of|Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of|National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of|National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore|National Centre for Infectious Diseases, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04292899
STUDY TO EVALUATE THE SAFETY AND ANTIVIRAL ACTIVITY OF REMDESIVIR (GS-5734™) IN PARTICIPANTS WITH MODERATE CORONAVIRUS DISEASE (COVID-19) COMPARED TO STANDARD OF CARE TREATMENT
Drug: Remdesivir|Drug: Standard of Care
Proportion of Participants Discharged by Day 14|Proportion of Participants With Treatment Emergent Adverse Events Leading to Study Drug Discontinuation
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
N=600
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 2020
May 2020
Providence Medical Research Center, Everett, Washington, United States|Swedish Center for Comprehensive Care, Seattle, Washington, United States|Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong|Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea, Republic of|Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of|National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of|National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore|National Centre for Infectious Diseases, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04292730
TETRANDRINE TABLETS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF COVID-19
Drug: Tetrandrine
Survival rate|body temperature
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
N=60
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 5, 2020-May 1, 2021
Tetrandrine Tablets, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04308317
IMMUNITY AND SAFETY OF COVID-19 SYNTHETIC MINIGENE VACCINE
Biological: Injection and infusion of LV-SMENP-DC vaccine and antigen-specific CTLs
Clinical improvement based on the 7-point scale|Lower Murray lung injury score|28-day mortality|Duration of mechanical ventilation|Duration of hospitalization|Proportion of patients with negative RT-PCR results|Proportion of patients in each category of the 7-point scale|Proportion of patients with normalized inflammation factors|Frequency of vaccine/CTL Events|Frequency of Serious vaccine/CTL Events
6 Months to 80 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1|Phase 2
N=100
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 24, 2020-December 31, 2024
Shenzhen Geno-immune Medical Institute, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04276896
BEVACIZUMAB IN SEVERE OR CRITICAL PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 PNEUMONIA-RCT
Drug: Bevacizumab
Proportion of patients whose oxygenation index increased by 100mmhg on the 7th day after admission
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
N=118
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Triple (Participant, Care Provider, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 12, 2020-May 31, 2020
Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04305106
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THALIDOMIDE IN THE ADJUVANT TREATMENT OF MODERATE NEW CORONAVIRUS (COVID-19) PNEUMONIA
Drug: thalidomide|Drug: placebo
Time to Clinical recoveryTime to Clinical Recovery (TTCR)|All cause mortality|Frequency of respiratory progression|Time to defervescence
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
N=100
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 20, 2020-June 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04273529
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THALIDOMIDE COMBINED WITH LOW-DOSE HORMONES IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE COVID-19
Drug: placebo|Drug: Thalidomide
Time to Clinical Improvement (TTCI)|Clinical status|Time to Hospital Discharge OR NEWS2 (National Early Warning Score 2) of ≤ 2 maintained for 24 hours|All cause mortality|Duration (days) of mechanical ventilation|Duration (days) of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation|Duration (days) of supplemental oxygenation|Length of hospital stay (days)|Time to 2019-nCoV RT-PCR negativity in upper and lower respiratory tract specimens|Change (reduction) in 2019-nCoV viral load in upper and lower respiratory tract specimens as assessed by area under viral load curve.|Frequency of serious adverse drug events|Serum TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, GSCF, IP10#MCP1, MIP1α and other cytokine expression levels before and after treatment
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
N=40
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 18, 2020-May 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04273581
FINGOLIMOD IN COVID-19
Drug: Fingolimod 0.5 mg
The change of pneumonia severity on X-ray images
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
N=30
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 22, 2020-July 1, 2020
Wan-Jin Chen, Fuzhou, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04280588
THERAPY FOR PNEUMONIA PATIENTS IINFECTED BY 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
Biological: UC-MSCs|Other: Placebo
Size of lesion area by chest imaging|Blood oxygen saturation|Rate of mortality within 28-days|Sequential organ failure assessment|Side effects in the UC-MSCs treatment group|Electrocardiogram, the changes of ST-T interval mostly|Concentration of C-reactive protein C-reactive protein, immunoglobulin|CD4+ and CD8+ T cells count|Concentration of the blood cytokine (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8,IL-10,TNF-α)|Concentration of the myocardial enzymes
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
N=48
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Triple (Participant, Care Provider, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 24, 2020-February 1, 2021
Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04293692
TREATMENT WITH MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS FOR SEVERE CORONA VIRUS DISEASE 2019(COVID-19)
Biological: MSCs|Biological: Saline containing 1% Human serum albumin(solution of MSC)
Improvement time of clinical critical treatment index within 28 days|Side effects in the MSCs treatment group|Proportion of patients in each classification of clinical critical treatment index|All cause mortality on Day 28|Invasive mechanical ventilation rate|Duration of oxygen therapy(days)|Duration of hospitalization(days)|Incidence of nosocomial infection|CD4+ T cell count by flow cytometry in two groups
18 Years to 70 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1|Phase 2
N=60
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 5, 2020-December 31, 2021
Wuhan Huoshenshan Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04288102
THE CLINICAL STUDY OF CARRIMYCIN ON TREATMENT PATIENTS WITH COVID-19
Drug: Carrimycin|Drug: lopinavir/ritonavir tablets or Arbidol or chloroquine phosphate|Drug: basic treatment
Fever to normal time (day)|Pulmonary inflammation resolution time (HRCT) (day)|Negative conversion (%) of 2019-nCOVRNA in gargle (throat swabs) at the end of treatment
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
N=520
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 23, 2020-February 28, 2021
Study Protocol, https://ClinicalTrials.gov/ProvidedDocs/03/NCT04286503/Prot_000.pdf|"Informed Consent Form", https://ClinicalTrials.gov/ProvidedDocs/03/NCT04286503/ICF_001.pdf
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04286503
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CORTICOSTEROIDS IN COVID-19
Drug: Methylprednisolone
the incidence of treatment failure in 14 days|clinical cure incidence in 14 days|the duration of virus change to negative|mortality at day 30|ICU admission rate in 30 days
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
N=400
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 14, 2020-May 30, 2020
Hubei province hospital of integrated Chinese & Western Medicine, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Yichang first people's Hospital, Yichang, Hubei, China|Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China|Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of science and technology, Wuhan, China|Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of science and technology, Wuhan, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04273321
SAFETY RELATED FACTORS OF ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION IN PATIENTS WITH SEVERE COVID-19 PNEUMONIA
Other: severe covid-19 pneumonia with ET
Success rate of intubation|Infection rate of Anesthesiologist|Extubation time
18 Years to 90 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
N=120
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Prospective
March 7, 2020-July 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04298814
Yinhu Qingwen Decoction for the Treatment of Mild / Common CoVID-19
Drug: YinHu QingWen Decoction|Drug: YinHu QingWen Decoction(low dose)|Other: Chinese medicine treatment|Other: standard western medicine treatment
Mean clinical recovery time (hours)|Time to CoVID-19 RT-PCR negative in upper respiratory tract specimen|Change (reduction) in CoVID-19 viral load in upper respiratory tract specimen as assessed by area under viral load curve.|Time to defervescence (in those with fever at enrolment)|Time to cough reported as mild or absent (in those with cough at enrolment rated severe or moderate)|Time to dyspnea reported as mild or absent (on a scale of severe, moderate, mild absent, in those with dyspnea at enrollment rated as severe or moderate)|Frequency of requirement for supplemental oxygen or non-invasive ventilation|Frequency of respiratory progression|Severe case incidence|Proportion of re-hospitalization or admission to ICU|All-cause mortality|Frequency of serious adverse events
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
N=300
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Double (Participant, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 27, 2020-January 2021
Jingzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jingzhou, Hubei, China|Wuhan Leishenshan (Thunder God Mountain) Hospital/The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Xiangyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xiangyang, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04278963
WASHED MICROBIOTA TRANSPLANTATION FOR PATIENTS WITH 2019-NCOV INFECTION
Other: washed microbiota transplantation|Other: placebo
Number of participants with improvement from severe type to common type
14 Years to 70 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
N=0
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 5, 2020-April 30, 2020
Medical Center for Digestive Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04251767
VARIOUS COMBINATION OF PROTEASE INHIBITORS, OSELTAMIVIR, FAVIPIRAVIR, AND CHLOROQUIN FOR TREATMENT OF COVID19 : A RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIAL
Drug: Oral
SARS-CoV-2 eradication time|Number of patient with Death|Number of patient with Recovery adjusted by initial severity in each arm|Number of day With ventilator dependent adjusted by initial severity in each arm|Number of patient developed Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome After treatment
16 Years to 100 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
N=80
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 15, 2020-November 30, 2020
Assistant Professor Subsai Kongsaengdao, Bangkok, Thailand
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04303299
PROGNOSITC FACTORS IN COVID-19 PATIENTS COMPLICATED WITH HYPERTENSION
Occupancy rate in the intensive care unit (ICU)|Mechanical Ventilation|Death|All cause mortality|Time from onset of symptoms to main outcome and its components|Time to Clinical Recovery
18 Years to 100 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
N=0
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
January 25, 2020-April 30, 2020
The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04272710
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND LONG-TERM PROGNOSIS OF 2019-NCOV INFECTION IN CHILDREN
The cure rate of 2019-nCoV.|The improvement rate of 2019-nCoV.|The incidence of long-term adverse outcomes.|Duration of fever|Duration of respiratory symptoms|Duration of hospitalization|Number of participant(s) need intensive care|Number of participant(s) with acute respiratory distress syndrome|Number of participant(s) with extra-pulmonary complications, including shock, renal failure, multiple organ failure, hemophagocytosis syndrome, et al.|Number of participant(s) who died during the trial
up to 18 Years (Child, Adult)
N=500
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 15, 2020-December 31, 2020
Beijing Children's Hospital,, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04270383
PROGNOSTIC FACTORS OF PATIENTS WITH COVID-19
all-cause mortality|Severe state
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
N=201
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
March 1, 2020-March 13, 2020
The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04292964
YINHU QINGWEN GRANULA FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE COVID-19
Drug: Yinhu Qingwen Granula|Drug: Yin Hu Qing Wen Granula(low does)|Other: standard medical treatment
changes in the ratio of PaO2 to FiO2 from baseline|PaO2|blood oxygen saturation (SpO2)|clinical status rating on the 7-point ordinal scale|Time to Clinical Improvement (TTCI)|Duration (hours) of non-invasive mechanical ventilation or high-flow nasal catheter oxygen inhalation use|Duration (hours) of invasive mechanical ventilation use|Duration (hours) of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) use|Duration (days) of Oxygen use|The proportion of the patients reporting 2019-nCoV RT-PCR negativity at Day 10 after treatment|The counts/percentage of Lymphocyte|Time to hospital discharge with clinical recovery from the randomisation|The incidence of critical status conversion in 30 days|All-cause mortality within 30 days|Frequency of severe adverse drug events
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
N=116
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
March 20, 2020-June 30, 2021
Wuhan No.7 Hospital/Jizhong Energy Fengfeng Group Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Wuhan No.7 Hospital/North China University of Science and Technology Affiliated Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University/Tanshan People's Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Wuhan Leishenshan (Thunder God Mountain) Hospital/The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04310865
CHLOROQUINE PREVENTION OF CORONAVIRUS DISEASE (COVID-19) IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING
Drug: Chloroquine|Drug: Placebo
Number of symptomatic COVID-19 infections|Symptoms severity of COVID-19|Duration of COVID-19|Number of asymptomatic cases of COVID-19|Number of symptomatic acute respiratory illnesses|Genetic loci and levels of biochemical components will be correlated with frequency of COVID-19, ARI and disease severity.
16 Years and older (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
10000
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Double (Participant, Investigator)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
May 2020
May 2022
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04303507
IMMUNOREGULATORY THERAPY FOR 2019-NCOV
Drug: PD-1 blocking antibody+standard treatment|Drug: Thymosin+standard treatment|Other: standard treatment
lung injury score|absolute lymphocyte counts|serum level of CRP, PCT and IL-6|SOFA score|all cause mortality rate|ventilation free days|ICU free days
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
120
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 10, 2020
October 31, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04268537
Sars-CoV2 Seroconversion Among Front Line Medical and Paramedical Staff in Emergency, Intensive Care Units and Infectious Disease Departments During the 2020 Epidemic
Other: blood sample
To assess the proportion of patients with documented Sars-CoV2 infection among medical and paramedical staff|Identification of risk factors for seroconversion|Quantify the proportion of asymptomatic infections among staff who have seroconverted|" Describe symptomatic infections for personnel developing acute clinical (respiratory or digestive) viral syndrome "
Child, Adult, Older Adult
Not Applicable
1000
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Other
March 11, 2020
October 12, 2020
Hopital Pitié Salpetrière, Paris, France
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04304690
EVALUATING THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF BROMHEXINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS COMBINED WITH STANDARD TREATMENT/ STANDARD TREATMENT IN PATIENTS WITH SUSPECTED AND MILD NOVEL CORONAVIRUS PNEUMONIA (COVID-19)
Drug: Bromhexine Hydrochloride Tablets|Drug: Arbidol Hydrochloride Granules|Drug: Recombinant Human Interferon α2b Spray|Drug: Favipiravir Tablets
Time to clinical recovery after treatment|Rate of aggravation|Clinical remission rate|Dynamic changes of oxygenation index|Time to cure|rate to cure|Time to defervescence|Time to cough remission|Time to dyspnea remission|Days of supplemental oxygenation|Rate of patients with requring supplemental oxygen|Rate of patients with mechanical ventilation|Time of negative COVID-19 nucleic acid results|Rate of negative COVID-19 nucleic acid results|Rate of ICU admission|28-day mortality
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
60
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Sequential Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 16, 2020
April 30, 2020
The Second AffIliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04273763
MILD/MODERATE 2019-NCOV REMDESIVIR RCT
Drug: Remdesivir|Drug: Remdesivir placebo
Time to Clinical recoveryTime to Clinical Recovery (TTCR)|All cause mortality|Frequency of respiratory progression|Time to defervescence (in those with fever at enrolment)|Time to cough reported as mild or absent (in those with cough at enrolment rated severe or moderate)|Time to dyspnea reported as mild or absent (on a scale of severe, moderate, mild absent, in those with dyspnoea at enrolment rated as severe or moderate,)|Frequency of requirement for supplemental oxygen or non-invasive ventilation|Time to 2019-nCoV RT-PCR negative in upper respiratory tract specimen|Change (reduction) in 2019-nCoV viral load in upper respiratory tract specimen as assessed by area under viral load curve.|Frequency of requirement for mechanical ventilation|Frequency of serious adverse events
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
308
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 12, 2020
April 27, 2020
Jin Yin-tan hospital, Wu Han, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04252664
MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL TREATMENT FOR PNEUMONIA PATIENTS INFECTED WITH 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
Biological: MSCs
Size of lesion area by chest radiograph or CT|Side effects in the MSCs treatment group|Improvement of Clinical symptoms including duration of fever and respiratory|Time of nucleic acid turning negative|Rate of mortality within 28-days|CD4+ and CD8+ T celll count|Alanine aminotransferase|C-reactive protein|Creatine kinase
18 Years to 70 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1
20
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
January 27, 2020
December 2021
Beijing 302 Military Hospital of China, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04252118
THE EFFICACY OF INTRAVENOUS IMMUNOGLOBULIN THERAPY FOR SEVERE 2019-NCOV INFECTED PNEUMONIA
Drug: Intravenous Immunoglobulin|Other: Standard care
Clinical improvement based on the 7-point scale|Lower Murray lung injury score|28-day mortality|Duration of mechanical ventilation|Duration of hospitalization|Proportion of patients with negative RT-PCR results|Proportion of patients in each category of the 7-point scale|Proportion of patients with normalized inflammation factors|Frequency of Adverse Drug Events|Frequency of Serious Adverse Drug Events
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
80
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 10, 2020
June 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04261426
A PROSPECTIVE/RETROSPECTIVE,RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED CLINICAL STUDY OF ANTIVIRAL THERAPY IN THE 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA
Drug: Abidol hydrochloride|Drug: Oseltamivir|Drug: Lopinavir/ritonavir
Rate of disease remission|Time for lung recovery|Rate of no fever|Rate of respiratory symptom remission|Rate of lung imaging recovery|Rate of CRP,ES,Biochemical criterion(CK,ALT,Mb) recovery|Rate of undetectable viral RNA
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
400
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 1, 2020
July 1, 2020
Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04255017
A PROSPECTIVE/RETROSPECTIVE,RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED CLINICAL STUDY OF INTERFERON ATOMIZATION IN THE 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA
Drug: Abidol hydrochloride|Drug: Abidol Hydrochloride combined with Interferon atomization
Rate of disease remission|Time for lung recovery|Rate of no fever|Rate of respiratory symptom remission|Rate of lung imaging recovery|Rate of CRP,ES,Biochemical criterion (CK,ALT,Mb)recovery|Rate of undetectable viral RNA
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
100
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 1, 2020
July 1, 2020
Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04254874
A RANDOMIZED,OPEN,CONTROLLED CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFICACY OF ASC09F AND RITONAVIR FOR 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA
Drug: ASC09F+Oseltamivir|Drug: Ritonavir+Oseltamivir|Drug: Oseltamivir
Rate of comprehensive adverse outcome|Time of clinical remission|Rate of no fever|Rate of no cough|Rate of no dyspnea|Rate of no need for oxygen inhalation|Rate of undetectable viral RNA|Rate of mechanical ventilation|Rate of ICU admission|Rate and time of CRP,ES,Biochemical criterion(CK,ALT,Mb)recovery
18 Years to 55 Years (Adult)
Phase 3
60
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 1, 2020
July 1, 2020
Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04261270
THE EFFICACY OF DIFFERENT HORMONE DOSES IN 2019-NCOV SEVERE PNEUMONIA
Drug: Methylprednisolone
Rate of disease remission|Rate and time of entering the critical stage|Rate of normal tempreture|Rate of respiratory symptom remission|Rate of lung imaging recovery|Rate of laboratory indicator recovery|Rate of undetectable viral RNA
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
100
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 1, 2020
July 1, 2020
Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04263402
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS DUE TO 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA WITH FUZHENG HUAYU
Drug: N-acetylcysteine+ Fuzheng Huayu Tablet|Drug: N-acetylcysteine+Placebo
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) score|Lung function including FVC, FVC as a percentage of projected value and DLco|Times of acute exacerbation|Six-minute walk distance|Dyspnea Scores|Composite physiological index
18 Years to 65 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
136
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Double (Participant, Investigator)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 15, 2020
December 2022
Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04279197
CT SCORES PREDICT MORTALITY IN 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA
Other: CT score
7-day mortality
Child, Adult, Older Adult
39
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
January 31, 2020
February 18, 2020
Wuhan third hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04284046
TREATMENT OF ACUTE SEVERE 2019-NCOV PNEUMONIA WITH IMMUNOGLOBULIN FROM CURED PATIENTS
Drug: Immunoglobulin of cured patients|Drug: γ-Globulin
Time to Clinical Improvement (TTCI)|Clinical status assessed by the ordinal scale|The differences in oxygen intake methods|Duration (days) of supplemental oxygenation|Duration (days) of mechanical ventilation|The mean PaO2/FiO2|The lesions of the pulmonary segment numbers involved in pulmonary CT [ every 7 days]|Time to 2019-nCoV RT-PCR negativity in respiratory tract specimens [every 3 days]|Dynamic changes of 2019-nCoV antibody titer in blood|Length of hospital stay (days)|All cause mortality
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
10
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 17, 2020
May 31, 2020
Department of Cardiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04264858
DEVELOPMENT AND VERIFICATION OF A NEW CORONAVIRUS MULTIPLEX NUCLEIC ACID DETECTION SYSTEM
Diagnostic Test: New QIAstat-Dx fully automatic multiple PCR detection platform
Sensitivity, spectivity turnaround time of the New QIAstat-Dx fully automatic multiple PCR detection platform
16 Years to 100 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
100
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
March 14, 2020
December 1, 2020
Huashan Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04311398
FAVIPIRAVIR COMBINED WITH TOCILIZUMAB IN THE TREATMENT OF CORONA VIRUS DISEASE 2019
Drug: Favipiravir Combined With Tocilizumab|Drug: Favipiravir|Drug: Tocilizumab
Clinical cure rate|Viral nucleic acid test negative conversion rate and days from positive to negative|Duration of fever|Lung imaging improvement time|Mortality rate because of Corona Virus Disease 2019|Rate of non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation when respiratory failure occurs|Mean in-hospital time
18 Years to 65 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
150
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 8, 2020
May 2020
Anhui Medical University Affiliated First Hospital, Hefei, Anhui, China|Guiqiang Wang, Beijing, Beijing, China|Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China|Cancer Hospital Union Hospital Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Ezhou Central Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Huoshenshan Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Jinyintan Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China|West Hospital Union Hospital Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04310228
NOVEL CORONAVIRUS INDUCED SEVERE PNEUMONIA TREATED BY DENTAL PULP MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
Biological: Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells
Disppear time of ground-glass shadow in the lungs|Absorption of Lung shadow absorption by CT Scan-Chest|Changes of blood oxygen
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Early Phase 1
24
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 5, 2020
July 30, 2021
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04302519
MULTICENTER CLINICAL STUDY ON THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF XIYANPING INJECTION IN THE TREATMENT OF NEW CORONAVIRUS INFECTION PNEUMONIA (GENERAL AND SEVERE)
Drug: Lopinavir / ritonavir tablets combined with Xiyanping injection|Drug: Lopinavir/ritonavir treatment
Clinical recovery time
18 Years to 100 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
80
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 14, 2020
April 14, 2021
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04295551
TOCILIZUMAB VS CRRT IN MANAGEMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME (CRS) IN COVID-19
Drug: Tocilizumab|Other: Standard of care|Procedure: Continuous renal replacement therapy
Proportion of Participants With Normalization of Fever and Oxygen Saturation Through Day 14|Duration of hospitalization|Proportion of Participants With Normalization of Fever Through Day 14|Change from baseline in white blood cell and differential count|Time to first negative in 2019 novel Corona virus RT-PCR test|All-cause mortality|Change from baseline in hsCRP|Change from baseline in cytokines IL-1β, IL-10, sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α|Change from baseline in proportion of CD4+CD3/CD8+CD3 T cells
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
120
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
February 20, 2020
June 20, 2020
Tongji Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04306705
THE EFFECT OF T89 ON IMPROVING OXYGEN SATURATION AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN PATIENTS WITH COVID-19
Drug: T89
The time to oxygen saturation recovery to normal level (≥97%)|The proportion of patients with normal level of oxygen saturation(≥97%)|The degree of remission of symptoms of patients, including: fatigue, nausea, vomiting, chest tightness, shortness of breath, etc.|The time to the myocardial enzyme spectrum recovery to normal after treatment|The proportion of the patients with normal myocardial enzyme spectrum after treatment|The time to the electrocardiogram recovery to normal level after treatment|The proportion of the patients with normal electrocardiogram after treatment|The time to the hemodynamics recovery to normal after treatment|The proportion of the patients with normal hemodynamics after treatment|The time to exacerbation or remission of the disease after treatment;|The proportion of the patients with exacerbation or remission of disease after treatment|The proportion of patients who need other treatment (e.g. heparin, anticoagulants) due to microcirculation disorders|The all-cause mortality rate|The proportion of patients with acidosis|The total duration of the patients in-hospital|The total duration of oxygen inhalation during treatment|The oxygen flow rate during treatment|The oxygen concentration during treatment
18 Years to 85 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
120
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 26, 2020
September 15, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04285190
RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL OF LOSARTAN FOR PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 REQUIRING HOSPITALIZATION
Drug: Losartan|Other: Placebo
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Respiratory Score|28-Day Mortality|90-Day Mortality|Respiratory Failure Requiring Mechanical Ventilation|Number of 28-Day Ventilator-Free Days|Length of Hospital Stay|ICU Admission|ICU Length of Stay|Acute Kidney Injury|Hypotension Requiring Vasopressors|Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Total Score|Severity Assessment|Incidence of Respiratory Failure|Oxygen Saturation / Fractional Inhaled Oxygen (F/S)
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
200
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 16, 2020
April 1, 2021
Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States|M Health Fairview University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States|University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04312009
RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL OF LOSARTAN FOR PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 NOT REQUIRING HOSPITALIZATION
Drug: Losartan|Other: Placebo
Hospital Admission|Change in PROMIS Dyspnea Functional Limitations|Change in PROMIS Dyspnea Severity|Fever Incidence Day 3|Fever Incidence Day 5|Fever Incidence Day 7|Fever Incidence Day 10|Severity of Symptoms upon Hospital Admission
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
478
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 16, 2020
April 1, 2021
Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States|M Health Fairview University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States|University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04311177
STUDY OF HUMAN UMBILICAL CORD MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS IN THE TREATMENT OF NOVEL CORONAVIRUS SEVERE PNEUMONIA
Biological: UC-MSCs|Drug: Placebo
Pneumonia severity index|Oxygenation index (PaO2/FiO2)|Side effects in the UC-MSCs treatment group|28-days survival|Sequential organ failure assessment|C-reactive protein|Procalcitonin|Lymphocyte count|CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T celll count|CD4+/CD8+ratio
18 Years to 65 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
48
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 16, 2020
February 15, 2022
Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04273646
CLINICAL STUDY OF ARBIDOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS IN THE TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA CAUSED BY NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
Drug: Arbidol|Other: basic treatment
Virus negative conversion rate in the first week|Virus negative conversion rate|Antipyretic rate|Symptom relief time|Finger oxygen improvement rate|Disease progression rate|Mortality rate|Incidence of severe adverse reactions|Change curve of peripheral blood lymphocyte count
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
380
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 7, 2020
December 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04260594
BEVACIZUMAB IN SEVERE OR CRITICAL PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 PNEUMONIA
Drug: Bevacizumab Injection
Partial arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) to fraction of inspiration O2 (FiO2) ratio|Degree of dyspnea (Liker scale)|Degree of dyspnea (VAS)|The area of lung lesions on Chest CT|The degree of lung exudation on Chest CT|SpO2|PaO2|CRP|hs-CRP|All-cause mortality
18 Years to 80 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
20
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 2020
May 2020
Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04275414
INTRAVENOUS AVIPTADIL FOR COVID-19 ASSOCIATED ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS
Drug: Aviptadil by intravenous infusion|Drug: Aviptadil by endotracheal nebulization
Mortality|PO2
18 Years to 100 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
20
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Crossover Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
April 2020
September 2020
Research Facility, New York, New York, United States|Rambam Health Care Campus, Haifa, Israel
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04311697
EVALUATION OF GANOVO (DANOPREVIR )COMBINED WITH RITONAVIR IN THE TREATMENT OF NOVEL CORONAVIRUS INFECTION
Drug: Ganovo+ritonavir+/-Interferon atomization|Drug: Long acting interferon|Drug: Recombinant cytokine gene-derived protein|Drug: Lopinavir+ritonavir|Drug: Chinese medicines +interferon atomization
Rate of composite adverse outcomes|Time to recovery|Rate of no fever|Rate of no cough|Rate of no dyspnea|Rate of no requiring supplemental oxygen|Rate of undetectable New coronavirus pathogen nucleic acid|Rate of mechanical ventilation|Rate of ICU admission|Rate of serious adverse event
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 4
50
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 17, 2020
April 30, 2020
The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04291729
EFFICACY OF A SELF-TEST AND SELF-ALERT MOBILE APPLET IN DETECTING SUSCEPTIBLE INFECTION OF COVID-19
Other: mobile internet survey on self-test
positive number diagnosed by national guideline in the evaluated population|distribution map of evaluated people|Effect of medical guidance by designated feedback questionnaire|mental scale of relief the mental anxiety and avoid unnecessary outpatient
Child, Adult, Older Adult
300000
Observational Model: Other|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 1, 2020
July 31, 2020
Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04256395
Nitric Oxide Gas Inhalation Therapy for Mild/Moderate COVID-19 Infection
Drug: Nitric Oxide
Reduction in the incidence of patients with mild/moderate COVID-19 requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation|Mortality|Negative conversion of COVID-19 RT-PCR from upper respiratory tract|Time to clinical recovery
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
240
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 13, 2020
April 1, 2022
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04305457
ADAPTIVE COVID-19 TREATMENT TRIAL
Other: Placebo|Drug: Remdesivir
Percentage of subjects reporting each severity rating on the 7-point ordinal scale|Change from baseline in alanine transaminase (ALT)|Change from baseline in aspartate transaminase (AST)|Change from baseline in creatinine|Change from baseline in glucose|Change from baseline in hemoglobin|Change from baseline in platelets|Change from baseline in total bilirubin|Change from baseline in white blood cell count|Change in National Early Warning Score (NEWS) from baseline|Cumulative incidence of serious adverse events (SAEs)|Cumulative incidence of severe adverse events (AEs)|Discontinuation temporary suspension of infusions|Duration of hospitalization|Duration of new mechanical ventilation|Duration of new oxygen use|Incidence of new mechanical ventilation|Incidence of new oxygen use|Mean change in the ordinal scale from baseline|Number of oxygenation free days|Number of ventilator free days|Subject clinical status using ordinal scale|Subject mortality|Time to an improvement of one category from admission using an ordinal scale|Time to discharge or to a National Early Warning Score (NEWS) of </= 2 and maintained for 24 hours, whichever occurs first
18 Years to 99 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
394
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Double (Participant, Investigator)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 21, 2020
April 1, 2023
University of California San Diego Health - Jacobs Medical Center, La Jolla, California, United States|University of California Irvine Medical Center - Infectious Disease, Orange, California, United States|University of California Davis Medical Center - Internal Medicine - Infectious Disease, Sacramento, California, United States|Emory Clinic - Investigational Drug Service, Atlanta, Georgia, United States|Emory Vaccine Center - The Hope Clinic, Decatur, Georgia, United States|University of Maryland School of Medicine - Center for Vaccine Development - Baltimore, Annapolis, Maryland, United States|Johns Hopkins Hospital - Medicine - Infectious Diseases, Baltimore, Maryland, United States|National Institutes of Health - Clinical Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Laboratory Of Immunoregulation, Clinical Research Section, Bethesda, Maryland, United States|University of Minnesota Medical Center, Fairview - Infectious Diseases and International Medicine, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States|Saint Louis University - Center for Vaccine Development, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States|University of Nebraska Medical Center - Infectious Diseases, Omaha, Nebraska, United States|Montefiore Medical Center - Infectious Diseases, Bronx, New York, United States|University of Texas Medical Branch - Division of Infectious Disease, Galveston, Texas, United States|Baylor College of Medicine - Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Houston, Texas, United States|EvergreenHealth Infectious Disease Service, Kirkland, Washington, United States|The University of Washington - Virology Research Clinic, Seattle, Washington, United States|Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, Washington, United States|Seoul National University Bundang Hospital - Division of Infectious Diseases, Bundang-gu Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, Republic of|Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Jongno-gu, Korea, Republic of|National Centre for Infectious Diseases (NCID), Singapore, Singapore
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04280705
NITRIC OXIDE GAS INHALATION THERAPY FOR MILD/MODERATE COVID19 INFECTION
Drug: Nitric Oxide
Reduction in the incidence of intubation and mechanical ventilation|Mortality|Negative conversion of COVID-19 RT-PCR from upper respiratory tract|Time to clinical recovery
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
240
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 1, 2020
February 1, 2022
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04290858
ECULIZUMAB (SOLIRIS) IN COVID-19 INFECTED PATIENTS
Drug: Eculizumab
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04288713
SEVERE 2019-NCOV REMDESIVIR RCT
Drug: Remdesivir|Drug: Remdesivir placebo
Time to Clinical Improvement (TTCI) [Censored at Day 28]|Clinical status|Time to Hospital Discharge OR NEWS2 (National Early Warning Score 2) of ≤ 2 maintained for 24 hours.|All cause mortality|Duration (days) of mechanical ventilation|Duration (days) of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation|Duration (days) of supplemental oxygenation|Length of hospital stay (days)|Time to 2019-nCoV RT-PCR negativity in upper and lower respiratory tract specimens|Change (reduction) in 2019-nCoV viral load in upper and lower respiratory tract specimens as assessed by area under viral load curve.|Frequency of serious adverse drug events
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
453
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 6, 2020
May 1, 2020
Bin Cao, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04257656
INFLUENCE OF THE COVID-19 EPIDEMIC ON STRESS
Stress|Perception and knowledge of the epidemic|Feeling of information on the part of companies / establishments / governments|Means of protection|Feelings of fear generated and its impact on feelings of stigmatization towards ethnic groups or categories of patients|Sociodemographic factors and lifestyle habits
Child, Adult, Older Adult
50000
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Cross-Sectional
March 11, 2020
March 2022
University Hospital, Clermont-Ferrand, Clermont-Ferrand, France
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04308187
BLOOD DONOR RECRUITMENT DURING EPIDEMIC OF COVID-19
Other: Questionnaire with precaution information|Other: Experimental: Questionnaire without precaution information
Differences of attitude about blood donation towards different questionnaires|Rates of blood donation during 3 weeks
18 Years to 60 Years (Adult)
Not Applicable
1500
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Health Services Research
March 12, 2020
April 9, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04306055
MEDICAL MASKS VS N95 RESPIRATORS FOR COVID-19
Device: Medical Mask|Device: N95 respirator
RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 infection|Acute respiratory illness|Absenteeism|Lower respiratory infection|Pneumonia|ICU admission|Mechanical ventilation|Death
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
576
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
April 1, 2020
January 1, 2021
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04296643
ACCURATE CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 PNEUMONITIS
survival status
Child, Adult, Older Adult
669
Observational Model: Other|Time Perspective: Retrospective
December 10, 2019
March 4, 2020
Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04302688
THE INVESTIGATION OF THE NEONATES WITH OR WITH RISK OF COVID-19
The death of newborns with COVID-19|The SARS-CoV-2 infection of neonates born to mothers with COVID-19|The Chinese standardized Denver Developmental Screening Test (DDST) in neonates with or with risk of COVID-19|The small for gestational age newborns in the neonates born to mothers with COVID-19|The preterm delivery of neonates born to mothers with COVID-19|The disease severity of neonates with COVID-19
up to 28 Days (Child)
100
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 1, 2020
December 31, 2020
Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Hubei Province, Wuhan, Hubei, China|Children Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04279899
NITRIC OXIDE GAS INHALATION FOR SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME IN COVID-19.
Drug: Nitric Oxide Gas
SARS-free patients at 14 days|Survival at 28 days|Survival at 90 days|SARS-free days at 28 days|SARS -free days at 90 days|Renal Replacement Therapy|Liver Failure|Mechanical Support of Circulation|PaO2/FiO2 ratio in ambient air
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
104
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Triple (Participant, Care Provider, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 1, 2020
March 1, 2022
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04290871
ANTI-SARS-COV-2 INACTIVATED CONVALESCENT PLASMA IN THE TREATMENT OF COVID-19
The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 1|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 3|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 7|Numbers of participants with different Clinical outcomes|Number of participants with treatment-related adverse events as assessed by CTCAE v5.0
Child, Adult, Older Adult
15
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 1, 2020
December 31, 2020
Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04292340
IDENTIFYING CRITICALLY-ILL PATIENTS WITH COVID-19 WHO WILL BENEFIT MOST FROM NUTRITION SUPPORT THERAPY: VALIDATION OF THE NUTRIC NUTRITIONAL RISK ASSESSMENT TOOL
Other: Nutrition support
28-day all cause mortality|All cause infection|The rate of complications|Length of ICU stay|Duration of mechanical ventilation
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
100
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 2020
July 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04274322
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF IFN-Α2Β IN THE TREATMENT OF NOVEL CORONAVIRUS PATIENTS
Drug: Recombinant human interferon α1β
The incidence of side effects|Time from patient enrollment to clinical remission|Proportion of patients with normal body|Proportion of patients without dyspnea|Proportion of patients without cough|Proportion|The negative conversion rate of new coronavirus nucleic acid|Frequency of serious adverse drug events.
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Early Phase 1
328
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 1, 2020
June 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04293887
DETECTION OF 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS IN MULTIPLE ORGAN SYSTEM AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Positive rate of 2019 Novel Coronavirus RNA|Survival rate
Child, Adult, Older Adult
20
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
January 20, 2020
February 28, 2021
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04279795
CLINICAL FEATURES OF SUSPECTED AND CONFIRMED PATIENTS OF 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS INFECTION
Other: Comprehensive treatment
Survival rate|Chest computed tomography|Recovery Time|Depression evaluation
Child, Adult, Older Adult
100
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
January 20, 2020
February 28, 2021
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04279782
CLINICAL PROGRESSIVE CHARACTERISTICS AND TREATMENT EFFECTS OF 2019-NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
Mortality|The time interval of Nucleic acid detection become negative
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
400
Observational Model: Other|Time Perspective: Retrospective
January 1, 2020
July 31, 2020
Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04292327
UMBILICAL CORD(UC)-DERIVED MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS(MSCS) TREATMENT FOR THE 2019-NOVEL CORONAVIRUS(NCOV) PNEUMONIA
Biological: UC-MSCs
Oxygenation index|28 day mortality|Hospital stay|2019-nCoV nucleic acid test|Improvement of lung imaging examinations|White blood cell count|Lymphocyte count|Lymphocyte percentage|Procalcitonin|interleukin(IL)-2|IL-4|IL-6|IL-8|IL-10|tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-α|γ-interferon(IFN)
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
10
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
February 6, 2020
September 30, 2020
Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04269525
EVALUATING AND COMPARING THE SAFETY AND EFFICIENCY OF ASC09/RITONAVIR AND LOPINAVIR/RITONAVIR FOR NOVEL CORONAVIRUS INFECTION
Drug: ASC09/ritonavir group|Drug: lopinavir/ritonavir group
The incidence of composite adverse outcome|Time to recovery|Rate of no fever|Rate of no cough|Rate of no dyspnea|Rate of no requring supplemental oxygen|Rate of undectable viral RNA|Rate of mechanical ventilation|Rate of ICU admission|Time and rate of laboratory indicators related to disease improvement to return to normal
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
160
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 7, 2020
June 30, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04261907
VITAMIN C INFUSION FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE 2019-NCOV INFECTED PNEUMONIA
Drug: VC|Drug: Sterile Water for Injection
Ventilation-free days|28-days mortality|ICU length of stay|Demand for first aid measuments|Vasopressor days|Respiratory indexes|Ventilator parameters|APACHE II scores|SOFA scores
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
140
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Triple (Participant, Care Provider, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 14, 2020
September 30, 2020
Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04264533
XIYANPING INJECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF NEW CORONAVIRUS INFECTED PNEUMONIA
Drug: Xiyanping injection|Drug: Lopinavir / ritonavir, alpha-interferon nebulization
Clinical recovery time|Complete fever time|Cough relief time|Virus negative time|Incidence of severe or critical neocoronavirus pneumonia
18 Years to 70 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
348
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 14, 2020
December 14, 2021
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04275388
DEVELOPMENT OF A SIMPLE, FAST AND PORTABLE RECOMBINASE AIDED AMPLIFICATION ASSAY FOR 2019-NCOV
Diagnostic Test: Recombinase aided amplification (RAA) assay
Detection sensitivity is greater than 95%|Detection specificity is greater than 95%|Consistent with existing universal reagent detection rates greater than 95%
1 Year to 90 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
50
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
January 1, 2020
December 31, 2020
Department of Hepatology Division 2, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04245631
SAFETY AND IMMUNOGENICITY STUDY OF 2019-NCOV VACCINE (MRNA-1273) TO PREVENT SARS-COV-2 INFECTION
Biological: mRNA-1273
Frequency of solicited local reactogenicity adverse events (AEs)|Frequency of any medically-attended adverse events (MAAEs)|Frequency of any new-onset chronic medical conditions (NOCMCs)|Frequency of any serious adverse events (SAEs)|Frequency of any unsolicited adverse events (AEs)|Frequency of solicited systemic reactogenicity adverse events (AEs)|Grade of any unsolicited adverse events (AEs)|Grade of solicited local reactogenicity adverse events (AEs)|Grade of solicited systemic reactogenicity adverse events (AEs)|Geometric mean fold rise (GMFR) in IgG titer from baseline|Geometric mean titer (GMT) of antibody|Percentage of subjects who seroconverted
18 Years to 55 Years (Adult)
Phase 1
45
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Sequential Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Prevention
March 3, 2020
June 1, 2021
Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute - Vaccines and Infectious Diseases, Seattle, Washington, United States
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04283461
2019-NCOV OUTBREAK AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
Cardiovascular Death|Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events|Times From symptom onset to hospital arrival|Anxiety
Child, Adult, Older Adult
N=12000
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Prospective
January 20, 2020
April 30, 2020
Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical Universty, Binzhou, Shandong, China|Heze Municipal Hospital, Heze, Shandong, China|Shandong University Qilu Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, China|Jinan Central Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China|First Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China|Shandong Provincial Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China|The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China|Jining Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jining, Shandong, China|Qihe People's Hospital, Qihe, Shandong, China|Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University Medical College, Qingdao, Shandong, China|Weihai Municipal Hospital, Weihai, Shandong, China|Central Hospital of Zibo, Zibo, Shandong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04255940
SOCIAL MEDIA USE DURING COVID-19
Behavioral: Use of social media during COVID-19
Assessment of COVID-19 situation|Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale|Familiarity and trust in COVID-related rumours|Availability heuristic
21 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
5000
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Cross-Sectional
March 8, 2020
May 31, 2020
Yale-NUS College, Singapore, Singapore
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04305574
MULTICENTER STUDY ON NOSOCOMIAL TRANSMISSION OF SARS-COV-2 VIRUS
Other: nosocomial infection/hospital acquired infection
nosocomial infection
Child, Adult, Older Adult
300
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
March 9, 2020
October 30, 2020
Service Hygiène, Epidémiologie et Prévention, Lyon, France|Service Hygiène, Epidémiologie et Prévention, Lyon, France
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04290780
NITRIC OXIDE GAS INHALATION FOR SARS-COV-2
Drug: Nitric Oxide Gas
Change of arterial oxygenation at 48 hours from enrollment|Time to reach normoxemia during the first 28 days after enrollment|Proportion of SARS-nCoV-2 free patients during the first 28 days after enrollment|Survival at 28 days from enrollment|Survival at 90 days from enrollment
18 Years to 99 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
200
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Participant)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
March 10, 2020
March 10, 2022
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04306393
A NEW SCREENING STRATEGY FOR 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS INFECTION
Diagnostic Test: Standard screening strategy|Diagnostic Test: New screening strategy
Screening accuracy|Cost-effectiveness analysis
Child, Adult, Older Adult
Not Applicable
230
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Screening
February 2020
March 2020
the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04281693
VIRAL EXCRETION IN CONTACT SUBJECTS AT HIGH/MODERATE RISK OF CORONAVIRUS 2019-NCOV INFECTION
Biological: 2019-nCoV PCR
Number of Participants with presence of 2019-nCoV in at least one of nasopharyngeal swab|For each participant, time (days) between the last contact with the laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV case and the first positive PCR|For each participant, time (days) between the first positive PCR and the first negative PCR|Number of Participants with presence of at least one of the following symptoms: fever > 38°C, asthenia/fatigue/malaise, headache, thrills/sweating, myalgia/aches, cough, dyspnea, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, diarrhe|Number of Participants with positive serology in the 90 days following last contact
Child, Adult, Older Adult
300
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 4, 2020
February 4, 2021
CIC 1425, Paris, France
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04259892
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF DARUNAVIR AND COBICISTAT FOR TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA CAUSED BY 2019-NCOV
Drug: Darunavir and Cobicistat
The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 7|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 3|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 5|Number of participants with treatment-related adverse events as assessed by CTCAE v5.0|The critical illness rate of subjects at weeks 2|The mortality rate of subjects at weeks 2
Child, Adult, Older Adult
Phase 3
30
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
January 30, 2020
December 31, 2020
Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai, China|Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04252274
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE FOR TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA CAUSED BY 2019-NCOV ( HC-NCOV )
Drug: Hydroxychloroquine
The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 3|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 5|The virological clearance rate of throat swabs, sputum, or lower respiratory tract secretions at day 7|The mortality rate of subjects at weeks 2|Number of participants with treatment-related adverse events as assessed by CTCAE v5.0|The critical illness rate of subjects at weeks 2
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 3
30
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 6, 2020
December 31, 2020
Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai, China|Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04261517
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINES (TCMS) ON 2019-NCOV INFECTION
Drug: Conventional medicines (Oxygen therapy, alfa interferon via aerosol inhalation, and lopinavir/ritonavir) and Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) granules|Drug: Conventional medicines (Oxygen therapy, alfa interferon via aerosol inhalation, and lopinavir/ritonavir)
Time to complete remission of 2019-nCoV infection-associated symptoms|The incidence of dyspnea with low oxygen saturation level and high respiratory rate|Number of subjects who develop complications of 2019-nCoV infection|Time to virus shedding|Time to improvement of abnormalities in Chest radiology|The evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) symptoms before and after treatment
14 Years to 80 Years (Child, Adult, Older Adult)
Not Applicable
150
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
January 22, 2020
January 22, 2021
The Fifth Medical Center, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04251871
A SURVEY OF PSYCHOLOGICAL STATUS OF MEDICAL WORKERS AND RESIDENTS IN THE CONTEXT OF 2019 NOVEL CORONAVIRUS PNEUMONIA
GHQ-12(general health questionnaire-12)|IES-R(Impact of Event Scale-Revised)
Child, Adult, Older Adult
N=30000
Observational Model: Case-Only|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 3, 2020
April 20, 2020
Tongji Hospital,Tongji Medical College Affiliated,Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04260308
Clinical Study of Anti-CD147 Humanized Meplazumab for Injection to Treat With 2019-nCoV Pneumonia
Drug: Meplazumab for Injection
2019 nCoV nucleic acid detection|Recovery of body temperature|Recovery of resting respiratory rate|Recovery of SPO2|Chest CT / chest film changes|PaO2 / FiO2|Time to reach the isolation release standard|Changes of inflammatory immune status
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1|Phase 2
20
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 3, 2020
December 31, 2020
Tangdu Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04275245
Acute Respiratory Failure and COVID-19 in Real Life
Other: standard operating procedures
Real life data of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection|in-hospital mortality|30 days mortality|6 months mortality|Intubation rate|Time to Intubation|Time to ventilation|Non invasive to Invasive time|Recovery rate|Recurrence rate|Risk factor for COVID19|Blood tests and outcome|Antiviral therapy|Coinfections|Radiological findings|Ultrasound findings|Myocardial injury|Medical management
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
50
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Prospective
March 19, 2020
December 31, 2020
Luigi Sacco University Hospital, Milan, Lombardia, Italy
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04307459
Stem Cell Educator Therapy Treat the Viral Inflammation in COVID-19
Combination Product: Stem Cell Educator-Treated Mononuclear Cells Apheresis
Determine the number of Covid-19 patients who were unable to complete SCE Therapy|Examine the percentage of activated T cells after SCE therapy by flow cytometry|Assess the percentage of Th17 cells after SCE therapy by flow cytometry|Chest imaging changes by computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest|Quantification of the SARS-CoV-2 viral load by real time RT-PCR
18 Years to 60 Years (Adult)
Phase 2
20
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Single (Care Provider)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
April 10, 2020
November 10, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04299152
EXPANDED ACCESS REMDESIVIR (RDV; GS-5734™)
Drug: Remdesivir
Child, Adult, Older Adult
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04302766
Sero-epidemiological Survey of England in 2019/2020 (STORY)
Procedure: venepuncture
Feasibility of developing a UK based sero-epidemiological programme in 0-24 year olds|Feasibility of developing a UK based sero epidemiological survey in 0-24 year olds|Recruitment
up to 24 Years (Child, Adult)
2300
Observational Model: Other|Time Perspective: Prospective
October 15, 2019
November 30, 2020
Centre for Clinical Vaccinology & Tropical Medicine (CCVTM), Oxford, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04061382
CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF PATIENTS WITH COVID19
Other: retrospective analysis
Time to negative conversion of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2|Length of stay in hospital|Survival|Intubation
Child, Adult, Older Adult
50
Observational Model: Cohort|Time Perspective: Retrospective
February 22, 2020
March 31, 2020
HuiZhou Municipal Central Hospital, Huizhou, Guangdong, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04280913
NK CELLS TREATMENT FOR NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
Biological: NK Cells
Improvement of clinical symptoms including duration of fever|Improvement of clinical symptoms including respiratory frequency|Number of participants with treatment-related adverse events evaluated with CTCAE,version 4.0|Time of virus nucleic acid test negative|CD4+ and CD8+ T cell count|Rate of mortality within 28-days|Size of lesion area by thoracic imaging
18 Years to 65 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1
30
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 20, 2020
December 30, 2020
The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, Henan, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04280224
GLUCOCORTICOID THERAPY FOR NOVEL CORONAVIRUSCRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
Drug: methylprednisolone therapy|Other: Standard care
Lower Murray lung injury score|The difference of PaO2/FiO2 between two groups|Lower Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score|Mechanical ventilation support|Clearance of noval coronavirus|All-cause mortality
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
80
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
January 26, 2020
December 25, 2020
Medical ICU,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, Beijing, China
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04244591
LOPINAVIR/ RITONAVIR, RIBAVIRIN AND IFN-BETA COMBINATION FOR NCOV TREATMENT
Drug: Lopinavir/ritonavir|Drug: Ribavirin|Drug: Interferon Beta-1B
Time to negative NPS|Time to negative saliva|Time to clinical improvement|Hospitalisation|Mortality|Immune reaction|Adverse events|Time to negative all clinical specimens
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2
70
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 10, 2020
July 31, 2022
University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04276688
POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR SARS-CORONAVIRUS-2
Drug: Hydroxychloroquine|Other: Placebo
Incidence of COVID19 Disease|Ordinal Scale of COVID19 Disease Severity|Incidence of Hospitalization|Incidence of Death|Incidence of Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Detection|Incidence of Symptoms Compatible with COVID19 (possible disease)|Incidence of All-Cause Study Medicine Discontinuation or Withdrawal
18 Years and older (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 2|Phase 3
1500
Allocation: Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
April 2020
May 2021
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04308668
French COVID Cohort (FrenchCOVID)
Clinical features|Response to treatment|Pathogen replication, excretion and evolution, within the host|Immune host responses to infection and therapy|Host genetic variants
Child, Adult, Older Adult
500
Observational Model: Other|Time Perspective: Prospective
February 7, 2020
August 7, 2023
CHU Pellegrin, service des Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales, Bordeaux, France|APHP La Pitié Salpêtrière, service des Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales, Paris, France|APHP Bichat, Service de réanimation médicale et infectieuse, Paris, France|APHP Bichat, Service des Maladies Infectieuses et Tropicales, Paris, France
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04262921
A PILOT CLINICAL STUDY ON INHALATION OF MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS EXOSOMES TREATING SEVERE NOVEL CORONAVIRUS PNEUMONIA
Biological: MSCs-derived exosomes
Adverse reaction (AE) and severe adverse reaction (SAE)|Time to clinical improvement (TTIC)|Number of patients weaning from mechanical ventilation|Duration (days) of ICU monitoring|Duration (days) of vasoactive agents usage|Duration (days) of mechanical ventilation supply|Number of patients with improved organ failure|Rate of mortality
18 Years to 75 Years (Adult, Older Adult)
Phase 1
30
Intervention Model: Single Group Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment
February 15, 2020
July 31, 2020
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04276987
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
COVID-19 Resources for Clinical Researchers and Students
COVID-19 Resources for Clinical Researchers and Students
At CCRPS, we will be continuing all remote learning courses for our students. We suggest you stay at home to review each module rather than at a library or coffee shop to protect both yourself and your family members. If you need an extension on your course due to the current events, please contact Dr. Desai at pdesai@ccrps.org any time.
We wanted to share resources which will help curious minds in clinical research (like ourselves) stay current with the quick changes occurring in response to COVID-19.
COVID-19 & Management - EMCRIT
This resource by Emergency Critical Care provides clinically relevant information on the pathophysiology, clinical diagnoses, testing, and potential treatments for COVID-19.
Mass General COVID-19 Grand Rounds
The Mass General Grand Rounds on 3/12/20 by the BCPR provides information on the Timeline of Spread, Epidemiology, COVID-19 pathophysiology, Vaccine development, Pharmacology, and more important topics needed to understand the current status of the pandemic.
Vaccine Trial for SARS COV-2
The Vaccine Trial is currently in Phase 1 with a current estimated end date of January 2021 at Kaiser in Seattle, WA. For those interested in a deeper dive into clinical trial management, consider the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification.
ClinicalTrials.Gov Trials for COVID-19
There are over 80 Clinical Trials being conducted for COVID-19 listed on the ClinicalTrials.gov website, useful for all clinical researchers to review. Enhance your expertise by exploring courses like Clinical Research Coordinator or Clinical Trials Assistant Training.
CDC COVID-19 Page
The CDC is the main source of clinical practice and laboratory practice guidelines relevant to all healthcare professionals. For those involved in drug safety, the Pharmacovigilance Certification could be of interest.
UptoDate Open Access Page on COVID-19
UptoDate has now made their COVID-19 page (draft; not completed peer-review) available with citations of important literature in the past few months. This is a great reference tool. For detailed guidelines and practices, consider the ICH-GCP Training.
We wish you well and hope you stay safe, practice social distancing as needed, and use this opportunity if home to learn more.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional. Discover more from Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course.
Additionally, for those looking to specialize further, explore the Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification and Medical Monitor Certification.
How Clinical Research Certification Could Help You Land a Job
Clinical research courses are very important for a variety of clinical research positions that require different skill sets. To find the right job opportunity, there are a number of key factors which you should consider while finding a training course.
As a clinical researcher, you should know your long-term and short-term goals. Then, you should develop the skill sets and gain the experience to reach them. For example, if your goal is to move in from a Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC) to a Clinical Research Associate (CRA), you should start building skills that a regional associate or a monitoring role would find valuable. Sometimes that can be as easy as taking on more diverse tasks at your current position, or taking an online CRA course.
Benefits of holding clinical research certification
According to the clinical association research profession, the evidence indicated to the regulatory bodies that certification reduces the risk factor to work in a research subjects.
It has been shown that trials have fewer errors, lower costs or more rapid turnaround, and higher safety in clinical trials when certified professional trainees are involved.
Certifications can help demonstrate to employers your confidence and abilities, as well as your long-term and short-term goals and how they might benefit the company. For CROs, employees with certifications will improve their company’s marketability and standards. Certification in areas like Pharmacovigilance or ICH-GCP can be particularly valuable.
Certification will make you more competitive in the industry to allow you to stand out.
If a company interviews you and another candidate with equal experience and education, their manager will be more likely to hire the candidate who has a certification.
If you have a certification, you can negotiate for higher salary. Getting certified, especially in specialized roles such as Clinical Trials Assistant Training, Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification, or Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification, will open more opportunities to you, where you can be hired for more senior and better paid positions within the company.
Even though there are enormous job vacancies in this field, employers will only hire skilled applicants that can do the job. A certification is a formal recognition for your skills, experience and performance. It will help validate your resume, especially when they are compared to other applicants’.
There are lots of clinical research online certification courses where you can study under best universities. To understand more, you can visit ccrps.org to understand their online certification course work, as well as any questions about the clinical research exam. Below, we have complied some helpful articles to help you excel in the field.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
Why Are So Many Student Taking Clinical Research Courses?
Clinical research courses are becoming a popular subject worldwide. Many students pick this course because of their interest in clinical health science but are drawn to research. The scope of the course is to help students evaluate and understand the new medicines and drugs that are used in clinical trials. This help students find jobs that deal with pharmaceutical products, diagnostic devices, drugs, medicines, and treatment tools.
What is clinical research?
Clinical research can be divided into animal and human trials. These trials help evaluate the effectiveness of drugs and ensure the safety of medical devices. To develop a plan, researchers need to ask questions like:
Which patient who undergo the trial?
When will the trial start?
What kind of treatment should be given?
How can we monitor the processes at every stage?
What is the duration of the whole study?
Researchers involved in these trials often require comprehensive training and certification, such as those offered through a Clinical Research Coordinator course or Pharmacovigilance Certification.
Benefits of clinical research courses
Clinical research helps change and redefine what is possible with medicine. People in clinical research do what they do because they know that their work can change someone’s life.
Clinical research courses have helped many aspiring students become capable professionals. In fact, those who have taken the course often were able to negotiate for more benefits and compensation. Advanced courses like Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification can further enhance career prospects.
How do I find the right course for me?
There are many institutions where one can successfully complete their course. Most courses are offered by health science oriented universities and medical schools. They are generally categorized into three types:
The undergraduate degree is open to students with basic schooling in health sciences. The duration of course study may be 3 to 4 years.
The master’s degree is open to life sciences, medicine, nursing, and pharmacology students. The duration of course study is 2 years.
The doctoral program is open for students with a postgraduate degree in life sciences or clinical research. In most universities, the entire duration of the course is 3 years.
For those looking to specialize further, certifications such as ICH-GCP, CRA, and Medical Monitor Certification provide targeted training for specific roles within clinical research.
When you are looking for a clinical research course, the best thing to do is find the best college. Research colleges based on information about the institution and the types of courses that they offer. You should especially inquire if the institution offers other medical programs. Browse some of our other articles below to get more information on clinical research education.
Remember, even as you become a professional, your education should never stop. CCRPS is here to ensure that you have all the tools you need to succeed. We offer online training courses that are accredited by ACCRE and are tailored to the position you want.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Navigating the World of Clinical Research Education
Courses:
Clinical Research Coordinator Course - Gain the essential skills and knowledge required to coordinate clinical trials effectively. Learn about trial planning, patient selection, treatment administration, and process monitoring.
Pharmacovigilance Certification Program - Explore the critical aspects of drug safety monitoring in clinical research. Understand the regulations, procedures, and reporting systems involved in pharmacovigilance.
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification - Elevate your career with advanced training in project management specific to clinical research. Learn to lead complex research projects, manage teams, and ensure efficient trial execution.
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification - Develop expertise as a principal investigator physician in clinical research. Acquire advanced knowledge in trial design, patient management, ethical considerations, and regulatory compliance.
ICH-GCP Certification - Obtain certification in Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines established by the International Council for Harmonisation. Understand the ethical and scientific quality standards for conducting clinical trials.
Certified Clinical Research Associate (CRA) Training - Prepare for a career as a clinical research associate responsible for monitoring and managing clinical trials. Learn about protocol compliance, data collection, and regulatory requirements.
Medical Monitor Certification - Specialize in medical monitoring roles within clinical research. Acquire expertise in safety assessment, adverse event reporting, and medical oversight during trials.
The Smart Way to Become a Pharmaceutical Research Associate
Many people are interested in working in the pharmaceutical sector. To break into the field, it is critical to look for relevant courses offered by reliable institutes. The search for the latest updates of top programs can help you make use of every chance to be successful in your career.
Pharmaceutical research associates around the world have a commitment to provide the best support and services. It is important for newcomers to understand the nature of their job and the importance of utilizing every opportunity to improve their expertise.
Focus on the Clinical Research Programs Online
Recently, many professionals in the medical sector join online programs to improve their professional expertise. In these programs, they network with other certified clinical research professionals and listen to courses designed for pharmaceutical research associates. In these online programs, you learn not only the fundamentals, but also the latest updates in the field. Online courses are valuable for newcomers who want to stand out from the crowd, as well as busy professionals who need their education at their own pace. Those interested in specific roles may consider the Clinical Research Coordinator course, the Pharmacovigilance Certification, or the CRA certification.
Join the Right Program
To find the right program, you can listen to clinical research program demos and compare them based on some significant factors like the course type, cost, benefits, and drawbacks. The best courses are accredited by reliable institutions and designed to fit your goals and lifestyle. At CCRPS, we offer ACCRE accredited courses that are designed by real field professionals. Additionally, our courses are quick and cost-effective. For those looking to expand their expertise further, consider our ICH-GCP course, Clinical Trials Assistant Training, Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification, or the Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification. For a specialized path, explore our Medical Monitor Certification.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
This integration adds the provided links at natural points in the existing content, where readers might be looking for specific courses or further details about opportunities in clinical research, without altering the original meaning or removing any existing links.
What Clinical Research Professionals Need to Know About CRT
Based on your instructions, I've added the relevant course links from CCRPS to the provided blog content. The links are inserted in appropriate sections without altering the original meaning of the content or removing any existing links. Here’s the updated content:
When people are interested in pursuing clinical research, they often need to take clinical research courses to become ready. In clinical research training program courses, students are trained in some common tasks such as clinical research billing, report writing, traits testing, and drug tests. In addition to all this, trainees are given a demo with equipment used in clinical research hospitals. Sometimes, lucky trainees are given a demo on CRT therapies.
CRT is known as cardiac resynchronization therapy. These therapies are done with a CRT pacemaker when patients have heart failure. In general, the CRT device comes in two types: CRT-P and CRT-D. In most cases, trainees can only demo the CRT-P device.
How does the CRT-P device work?
CRT-P consists of two components: the pulse generator and thin insulating wires. This device delivers tiny electrical signals to the left and right side of arteries and ventricles via leads, which makes the heart contract and pump like a normal heartbeat.
CRT-P devices are similar to normal pacemakers, delivering small signals to leads which make the ventricles contract at a normal rate.
The CRT-P device has a battery that is built within the device. When the CRT-P battery runs out, it is necessary to replace the entire device.
The battery limit is determined by a doctor based on what kind of therapy you need.
Although the device is good at providing efficient heart beat rate, when patients are done with the CRT-P pacemaker, there are several drawbacks also. Patients need to have regular checking on batteries of the CRT-P pacemaker device. The doctors would need to check the remaining energy in the device.
Moreover, there are some risks after the implantation of the CRT-P device, such as irritation of the skin all around where the device is placed. There also are several chances for place movements. If you wish to have further updates on clinical research training courses and medical equipment details then you can visit Clinical Research Coordinator courses at CCRPS.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more about how to become a clinical research professional. You can start with our Pharmacovigilance Certification or explore other opportunities like CRA Certification, ICH-GCP Training, Clinical Trials Assistant Training, Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification, and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification. For those looking into monitoring roles, our Medical Monitor Certification might be the perfect fit.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course.
Why You Should Take ASH CRTI With Your Clinical Research Course
When it comes to CRTI or clinical research training institute, trainees would learn valuable lessons in topics such as clinical research billing process and traits testing. All these would help them in pursuing clinical research jobs. For those looking to specialize further, the Clinical Research Coordinator course or the Clinical Trials Assistant Training offered by CCRPS can be a great addition to your professional training.
ASH CRTI is the American Society of Hematology, which has developed a clinical research training institute where trainees get experience from senior faculties related to patient oriented clinical research (POCR).
What made ASH CRTI differ from other CRTIs?
ASH clinical research training institute, or ASH CRTI, is a unique training given for people who need to be an early POCR investigator for one whole year. Here, about 20 trainees per year are trained by senior and junior faculty mentors. Here are some of the major components of the ASH clinical research training institute course are listed below:
Workshops will be conducted for a week in California, where trainees will learn about methodologies, foundations and patient-oriented clinical research applications. For those interested in regulatory standards and best practices in clinical research, consider the ICH-GCP course.
After a week of workshops, trainees would follow up for ASH annual meetings where they can listen to experiences from previous scholars. Those aiming for higher responsibility roles might find the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification useful.
A special one-day class would be conducted at the headquarters of ASH, which is located in Washington, DC. To prepare for such high-level interaction, the Medical Monitor Certification could provide essential insights.
Trainees would be given in-person meetings where they would be taught about networking and mentorship via distance learning. For more comprehensive training in drug safety, the Pharmacovigilance Certification is recommended.
In addition to one-on-one conversations with representatives and training faculties, trainees would have further interactions with their small trainee group along with mentors throughout the year. This interaction would ensure effective research collaborations and career development. Those looking to lead clinical trials might be interested in the Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification.
When people take ASH CRTI training along with CRTI course, they have additional resources for success in clinical research. If you wish to get more details about the ASH training course then you can visit ccrps.org.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional. Consider enhancing your career by becoming a Certified Research Associate (CRA).
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
What is the Purpose of Getting CRC certification?
Clinical research plays a predominant role in the field of medical science, and there are a wide range of career opportunities available. To start a career in clinical research, getting CRC certification which is highly useful for getting a job as a clinical research coordinator. Interested in this pathway? Consider the Clinical Research Coordinator course to begin your certification process.
What is a clinical research coordinator?
Clinical research coordinators or CRCs are specialized, entry-level research professionals responsible for conducting clinical trials according to the GCP guidelines. Many people enter the field through this position. Their main responsibility is to take care of the well-being of patients who are participating in a study. Enhance your understanding and skills in this area with our ICH-GCP course.
Getting CRC certificated means taking a course on how to be an effective CRC and passing an exam. It helps you apply for clinical research coordinator jobs, as it adds value to your qualifications and makes you more eligible for the position. Completing the CRC certification shows that the person has met the necessary requirements for the job.
Experience for becoming a clinical research coordinator
It seems hard to find experience in a job you might have no qualifications for, but it can be done with prior planning. While undergoing a CRC certification program, consider the Clinical Trials Assistant Training to get some experience on the job. Opting to volunteer for patient recruitment is a great way of getting valuable field experience that will impress big employers.
Skills required for becoming a clinical research coordinator
To make a career as a clinical research coordinator, you need a foundation in life sciences or other related fields. You also need to have a thorough understanding of the drug development process and ICH-GCP, which is often taught in CRC courses.
The job also requires excellent interpersonal and communication skills. In addition, multi-tasking and effective problem-solving skills are highly desired by employers. For those looking to advance further, the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification can be excellent next steps.
Use online for finding a job as a clinical research coordinator
If you are looking for clinical research coordinator jobs, make use of online clinical research headhunters who know the vacancies in top companies. This can help you find a position with a great company and receive great benefits. Apply for the job after checking the description of the position so that you can learn the requirements the employer is looking for and prepare well. Start up a career as a clinical research coordinator and find a great opportunity to work in the field of clinical research. For those with specific interest in drug safety, the Pharmacovigilance Certification may also be relevant.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional. Expand your expertise and qualifications by becoming a Certified Research Associate (CRA).
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
What is a Clinicals Research Specialist
Clinical research specialists play a pivotal role in the realm of healthcare, collaborating within laboratory settings alongside technologists, technicians, and supervisors to conduct crucial clinical lab tests. These professionals are instrumental in the discovery, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various illnesses. While their specific responsibilities may vary based on training and workplace, they typically focus on specialized lab tests or procedures, such as bacteria or parasite identification, fluid analysis, drug level testing, specimen preparation, cell counting, and culture creation. Apart from technical proficiency, they are equipped with essential communication, interpersonal, individualized, and precision skills.
JOB SPECIFICS OF A CLINICAL RESEARCH SPECIALIST
Enrollment Tracking and Documentation: Clinical research specialists meticulously track the enrollment status of subjects and document dropout information to ensure study integrity.
Continuous Learning: They stay abreast of the latest developments in clinical studies by reviewing scientific literature, attending conferences, and seminars.
Problem Identification and Resolution: Identifying protocol issues, informing investigators, and contributing to problem resolution efforts are integral aspects of their role.
Documentation Preparation: These professionals prepare various study-related documents, including protocol worksheets, procedural manuals, adverse event reports, and progress reports.
Collaboration: They collaborate with healthcare professionals to devise effective recruitment strategies for studies.
Quality Assurance: Participating in quality assurance audits and managing research budgets are part of their responsibilities.
Protocol Review: Reviewing proposed study protocols and assessing factors like sample collection processes and subject eligibility is crucial.
Subject Recruitment: Assessing potential subjects' eligibility, developing advertising materials, and maintaining contact with sponsors for recruitment purposes are key tasks.
Salary Insights: The national average salary for clinical research specialists is $52,437.
Clinical research specialists have diverse employment opportunities, including roles in:
Pharmaceutical companies
Government-based organizations like the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
Health charities
If you aspire to join this dynamic field, consider enhancing your skills and knowledge with courses from CCRPS (Clinical Research Professional Society). Explore our comprehensive offerings to embark on a fulfilling career journey:
Clinical Research Coordinator: Course Link
Pharmacovigilance Certification: Course Link
CRA (Clinical Research Associate): Course Link
ICH-GCP (International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use - Good Clinical Practice): Course Link
Clinical Trials Assistant Training: Course Link
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification: Course Link
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification: Course Link
Medical Monitor Certification: Course Link
Enroll today and pave your way to a successful career in clinical research!
What is the Best CRA Training Program for You?
To any CRA, proper training and certification is critical. After all, employers want to hire applicants that are proficient and knowledgeable. At CCRPS, we can help jump start your career with our flexible, ACCRE accredited program. In addition, check out some of our other CRA articles below to learn more about the field and position.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Enhance Your Skills with Specialized Training:
If you're looking to specialize in specific areas within clinical research or further develop your expertise, consider enrolling in our comprehensive courses:
Clinical Research Coordinator: Dive deep into the responsibilities and intricacies of coordinating clinical trials. Enroll here.
Pharmacovigilance Certification: Master the principles and practices of drug safety monitoring. Enroll here.
CRA (Clinical Research Associate): Hone your skills as a CRA and excel in managing clinical trial conduct. Enroll here.
ICH-GCP (International Conference on Harmonisation - Good Clinical Practice): Understand the global standards for conducting clinical trials. Enroll here.
Clinical Trials Assistant Training: Learn the essentials of supporting clinical trial operations effectively. Enroll here.
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification: Elevate your career with advanced project management skills tailored to clinical research. Enroll here.
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification: Equip yourself with the expertise needed to lead clinical trials as a principal investigator. Enroll here.
Medical Monitor Certification: Gain the necessary skills to oversee clinical trial safety and medical aspects effectively. Enroll here.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
An Overview of Covance CRO Clinical Research I Covance Clinical Trials
Covance CRO
With the increasing demand for skilled professionals in clinical research, it's imperative to consider courses that can equip individuals with the necessary expertise. Covance, as a renowned clinical research organization (CRO), underscores the importance of having trained personnel to ensure the safety and efficacy of clinical trials.
For those aspiring to venture into clinical research, courses such as Clinical Research Coordinator and Pharmacovigilance Certification can provide fundamental knowledge and skills. These courses cover essential aspects of clinical trial management and drug safety, preparing individuals to contribute effectively to research endeavors. Similarly, the CRA (Clinical Research Associate) course equips learners with the expertise needed to monitor clinical trials according to regulatory standards, including the International Conference on Harmonisation - Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP) guidelines.
Moreover, individuals interested in supporting clinical trials as assistants can benefit from specialized training programs like Clinical Trials Assistant Training. These courses offer insights into the administrative and logistical aspects of clinical research, enhancing participants' ability to contribute to the smooth conduct of trials.
For those seeking advanced roles in clinical research management, certifications such as Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician provide comprehensive training in leadership, project management, and regulatory compliance. These certifications are valuable assets for professionals aspiring to take on leadership positions within the clinical research industry.
Furthermore, specialized roles such as Medical Monitor Certification cater to professionals involved in overseeing the medical aspects of clinical trials, ensuring participant safety and protocol adherence.
By enrolling in these courses, individuals can acquire the necessary qualifications and skills to thrive in the dynamic field of clinical research, contributing to the advancement of medical science and improving human health.
Explore our courses: Clinical Research Coordinator
Pharmacovigilance Certification
Clinical Trials Assistant Training
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification
Covance Clinical Trials
Clinical trials go through carefully planed phases to reliably verify a drug. Any medicine available from your local pharmacy are the result of cumulative efforts of volunteer Participants. Without them, medical science will grind to a halt.
Covance is dedicated to delivering solutions and advancing the healthcare sector. This company has decades of expertise and precision in this field. If you are interested in how you can volunteer for a study, you can check out their website here.
Explore COVANCE’s broad range of specialized services:
Preclinical Reach IND/CTA quickly with a programmatic approach or choose from thousands of studies.
Clinical Trials Remove roadblocks to early & late trials with intelligent recruitment, integrated project delivery and therapeutic expertise.
Post-Marketing Solutions Maximize your product’s value and ensure patients have access to safe and effective treatments.
Clinical Trial Laboratory Services Comprehensive laboratory support for all phases of clinical trials.
Chemical & Crop Protection Meet global crop protection and chemical guidelines with expertise paired with regulatory insights.
Medical Devices Leverage a specialized team and powerful collection of resources for every step of product development.
Improve clinical study outcomes with unrivaled, proprietary data and technology.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
Clinical Research and Healthcare
Clinical research is part of the health care science that define the care and effectiveness of the medication, it’s devices and diagnostic products and treatment procedures that intended for human use.
Clinical research is a part of healthcare science and it determines how effective and safe diagnostic products, devices, and medications really are. Basically, it studies things that can be used for the diagnosis, treatment, and even prevention of diseases.
Clinical research is very different from other clinical practices. In clinical practice, the focus is on treatments already in use. In clinical research, evidence and innovation is creating new treatments for clinical practice.
The Scope
Clinical research is a broad term that refers to the study and testing of biologics, devices, and drugs. It includes any tests from lab inception all the way to introduction to the market.
First, a molecule or candidate to be tested has to be identified first. This is usually happening in a lab. Pre-clinical studies are then done on the chosen candidate, and then tested on animals. This is where efficacy and toxicity are determined and studied before being tested on humans.
Due to the risks, clinical research has to be authorized by the necessary bodies. A lot of supervision and care has to be taken to ensure that all test subjects are well taken care of and safe. This is because trials need to be conducted on humans, healthy or otherwise, before any drug is approved for market and mass consumption.
Where is it conducted?
In most cases, this kind of research is done at medical centers, especially the academic ones. There are also affiliated study sites that can be used. The sites are situated in areas where there is a high chance of getting many medical participants. There are review boards and regulatory bodies, such as the FDA, that make sure that clinical research is carried out in an ethical manner.
Clinical research involves a very complex network and all have to work for the benefit of everyone. To learn more, check out our website CCRPS.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
To learn more about how you can become a clinical research professional, visit our website and explore our diverse range of courses.
Explore our courses: Clinical Research Coordinator
Pharmacovigilance Certification
Clinical Trials Assistant Training
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification
Clinical Research Managers: Principal Responsibilities and Duties
Responsibilities and Duties
Clinical research managers are involved with the monitoring of all processes in clinical trials. They oversee the administration and staff of such trials. For example, they need to supervise the CRAs on-site and in-house monitoring and filing of the trials.
When one is a clinical research manager, it means that they have to oversee those FD regulations, good clinical practice, and SOPs are all adhered to. They are also required to offer assistance in the development and implementation of different clinical, programs, procedures, and processes.
Qualifications
Certification is very important in any career. For clinical research managers, they need to complete very specific professional exams. This is determined as per the region, by the rules set by the regulatory bodies For instance, in some areas a clinical research manager needs to have a nursing master’s degree.
First level managers
First level managers have to ensure that all the department or project milestones and goals are all met while sticking to the budgets approved by the top management. They must have the most extensive knowledge about the department, since they operate with all their processes. In most cases, clinical research managers need 5 years of experience in a particular field before moving up to more senior positions.
Clinical trial manager
These managers supervise and execute clinical trials. They also guide and oversee the clinical data managers and clinical research associates. Clinical trial manager needs to report to the CPM or the clinical project manager.
Explore our courses: Clinical Research Coordinator
Pharmacovigilance Certification
Clinical Trials Assistant Training
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
Clinical Trial Research Aimed at Assessing Behavioral, Surgical, and Medical Intervention
Clinical trials research are studies that are carried out on people. They are usually aimed at the evaluation of behavioral, surgical, and medical intervention. For example, there are different ways that researchers apply clinical research to discover something new about a medical device, diet, or even drugs. Others aim at identifying diseases as early even before any symptoms are evident. They are used to find ways in which health problems can be prevented. Additionally, clinical trials may also be conducted to find ways in which life can be better for persons who are living with diseases that are life-threatening or people with chronic health issues.
What is done before approval?
Before any clinical trial research is approved, laboratory tests have to be conducted by qualified scientists.
Studies are first done on animals subjects. This is done to test the therapy’s potential efficacy and safety. If favorable results are achieved, then the necessary regulatory body can give approval for it to be tested on human subjects.
The phases
The advancement of clinical trials research covers different phases to understand the dosage and identify side effects. When these four phases are complete and the drug or device is seen as favorable, then it receives approval for mass use. However, researchers will continue monitoring the product even after it is introduced in the market.
During phase one, tests are done on healthy people, but in a small group to find the correct dosage, and side effects.
The second phase involves more people and this time the aim is to find the treatment or device’s effectiveness. It offers data on whether a condition or disease can be combated by the drug.
The third phase is about effectiveness and safety. Different dosages and different populations are tested. The drug can be combined with others to see how that impacts the body. This is the point where the product gets FDA approval.
In phase four, after approval, the safety, and effectiveness of the device or drug are tested on a more diverse population for long term effects and monitored after it goes on the market.
Explore our comprehensive range of courses designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in clinical research:
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course
CNR: What Should Clinical Research Nursing Students be Reading
As an aspiring clinical research professional, it is important to stay up to date with what is happening in your field. Clinical Nursing Research (CNR) is a journal that covers clinical nursing. It is released four times a year and addresses clinical issues meaningful to nursing students. It also opens an international forum provide room to:
Spread widely findings of a particular research to practicing nurses.
Improve clinical practice by identifying clinical application that conforms to the latest research.
Encourage clinical practitioners among themselves.
CNR is one of the most important resources for clinicians and researchers who are concerned with improving their work. In addition, CNR provides graduates and undergraduates in the field of clinical nursing research with a source of field insights that will impress future employers and coworkers.
Features involved
Clinical nursing research offers some articles and features such as:
Feature articles with international references: this will enhance your understanding of the full scope of international research.
Articles researched: This involves discussions on a research project’s findings
Brief your research: short research reports on specific aspects of practice.
Replicated studies: These studies compare new findings with the existing ones, thereby providing important information to clinicians. This forms the basis for introduction of findings.
Who does the research?
CNR is written by a clinical nurse specialist. Their aim is to increase the standard of patient care. They also focus on finding a new treatment for different diseases. The nurses make sure that the patients are well protected and well supported during the period of study.
At CCRPS, in addition to ACCRE-certified courses, we also offer in-depth guide on how you can succeed in the clinical research field. Check below to sample some of our nursing articles.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
At CCRPS, we offer ACCRE-certified courses to help you excel in the clinical research field. Enhance your skills and knowledge with our comprehensive courses:
Clinical Cancer Research and Areas That Hold Interest
Clinical Cancer Research is a peer-reviewed medical journal based on oncology. It includes therapy, diagnosis, prevention, molecular and cellular characterization of human cancer. It also covers topics like clinical generics, surgical oncology, pathology, pediatric oncology, radiation therapy, and hematological oncology.
What it entails
The publication elaborates on the application of different disciplines of molecular, cell biology, and immunology genetics in the integration of cancer in humans. The main areas of interest are the clinical trials, which evaluate of the new treatments available to predict resistance and response.
Animal and laboratory studies of molecule targeted agents and drugs that have potential too. It focuses on studies of metastatic disease, malignant phenotype progression, and oncogenesis of targetable mechanisms.
The journal issues and what they cover
Clinical Cancer Research has been in publication since 1995. Publications have been submitted by all sorts of investigators, who represent disciplines like clinical and laboratory all over the world. Countless translational and innovative clinical cancer studies have been published in order to bridge clinic and laboratory. This is a journal that holds interest in the clinical trials that evaluate any new treatment. This is especially true when it comes to pharmacology research and molecular alterations.
Other interest areas include:
Human tumors molecular characterization
Radiation and radiobiology oncology
Gene therapy
Clinical and immunotherapy immunology
Application of biostatistics and bioinformatics personalized medicine
Pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics
Expand your knowledge and expertise in oncology research with CCRPS courses:
Clinical Research Coordinator: Course Link
Pharmacovigilance Certification: Course Link
CRA (Clinical Research Associate): Course Link
ICH-GCP (International Conference on Harmonization - Good Clinical Practice): Course Link
Clinical Trials Assistant Training: Course Link
Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification: Course Link
Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification: Course Link
Medical Monitor Certification: Course Link
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional.
Discover more from Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course